Understanding Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence affects millions of people worldwide, but it doesn't have to control your life.Take charge of your bladder health and live a more confident life and be able to control urination.

Have you ever experienced an embarrassing moment due to unexpected urine leakage? Do you think you have a weak bladder because you urinate frequently? Do you suffer with an overactive bladder and leak urine? You're not alone.
Urinary incontinence affects millions of people worldwide, but it doesn't have to control your life. In this blog post, we'll dive deep into understanding urinary incontinence, its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies. By the end, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to take charge of your bladder health and live a more confident life and be able to control urination.
Short Summary
- Urinary incontinence and urinary frequency is a common condition in older women that can be managed with the right treatment and lifestyle changes.
- Treatments include home remedies, pelvic floor exercises (Kegels), medications, medical devices, surgery and prevention strategies such as maintaining a healthy weight.
- If you're experiencing urinary incontinence, don't hesitate to seek professional help for diagnosis & treatment plan for your bladder control problem.
Understanding Urinary Incontinence

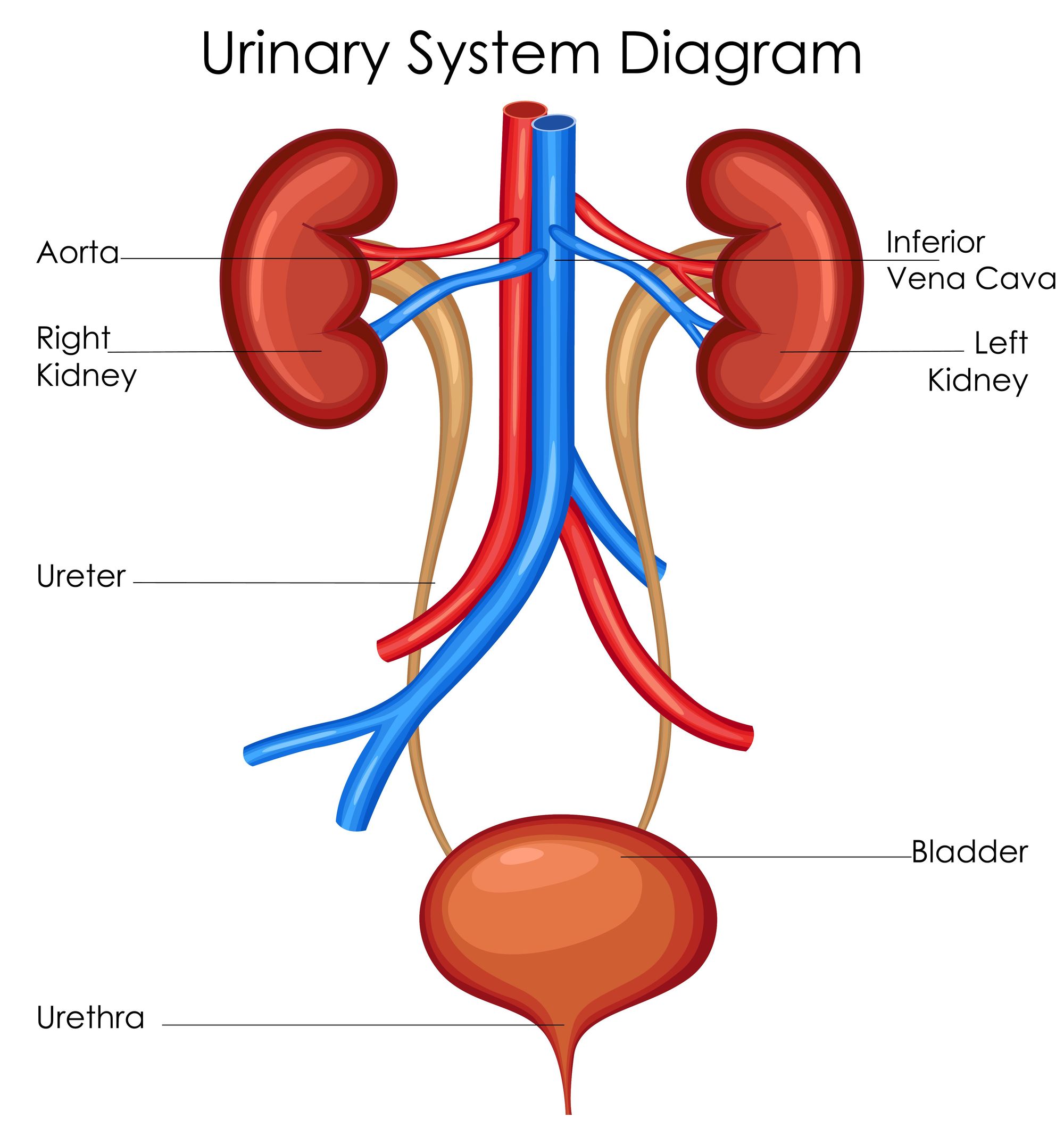
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine, which can range from a minor nuisance to a significant disruption in daily life. It occurs when the pelvic floor muscles, responsible for bladder control, weaken or become overactive. This can lead to various types of incontinence, such as stress incontinence, urge incontinence, and overflow incontinence. These issues may result from numerous factors, including age, pregnancy, obesity, and medical conditions like urinary tract infections.
Women are more likely to experience urinary incontinence than men, especially as they age. More than 4 in 10 women aged 65 and older suffer from urinary incontinence. This indicates that it is a common medical condition among older women. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, many people can regain control over their bladder and significantly improve their quality of life.
Common Types of Urinary Incontinence
There are three common types of urinary incontinence: stress incontinence, urge incontinence, and overflow incontinence. There is even a mixed incontinence. That means you have more than one type of incontinence issues. Each type has its own unique set of symptoms and causes. We'll explore these in the following subsections.
Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence occurs when weak pelvic muscles allow urine to leak during activities that put pressure on the bladder, such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, or exercising. It is often triggered by pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, obesity, and certain medical conditions that weaken the pelvic floor muscles.
To manage stress incontinence, doctors may recommend lifestyle modifications, pelvic floor exercises (Kegels), medications, medical devices, or even surgical treatments. These solutions aim to reduce stress incontinence, strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and restore bladder control.
Urge Incontinence
Urge incontinence, also known as overactive bladder, is characterized by a sudden, strong urge to urinate followed by involuntary urine leakage. It is typically caused by damage to the nerves of the bladder, the nervous system, the bladder muscle or the muscles that control bladder function.
Treatments for urge incontinence include lifestyle modifications, pelvic floor exercises, medications, medical devices, and surgery. These interventions aim to regain control over the bladder muscles and reduce the frequency of the sudden urge to urinate.
Overflow Incontinence
Overflow incontinence occurs when the bladder cannot store as much urine as the body is producing or cannot empty completely, leading to small amounts of urine leakage. Symptoms of overflow incontinence include frequent urination and a constant dripping of urine from the urethra.
Treatment options for overflow incontinence include lifestyle changes, medications, and medical devices. These approaches aim to improve bladder function and help the bladder empty more fully.
Mixed Incontinence
Mixed incontinence is a type of urinary incontinence that combines two or more types of incontinence. It occurs when you experience symptoms of both stress and urge incontinence simultaneously, making it difficult to identify the root cause.
The bladder is the organ responsible for storing urine until you are ready to empty it. To remain healthy, it is important to maintain a steady flow of urine and void regularly. If the bladder becomes weakened or overactive due to medical conditions such as diabetes or an enlarged prostate, it can cause mixed incontinence. Certain medications, lifestyle changes, and even surgery may be necessary to treat this condition.
Risk Factors and Causes

Certain risk factors make an individual more prone to developing urinary incontinence. Age is a significant factor, as the bladder and urethra muscles tend to lose strength over time. Pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause are also common contributors to urinary incontinence in women, as these events can affect the pelvic floor muscles and hormone levels. Obesity can put extra pressure on the bladder, leading to incontinence.
For men, an enlarged prostate gland can cause urinary incontinence by obstructing the bladder neck, preventing proper urine flow. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such kidney diseases such as multiple sclerosis and diabetes, can interfere with nerve signals and cause bladder control problems.
Signs and Symptoms

The signs and symptoms of urinary incontinence vary depending on the type and cause. For stress incontinence, the most common symptom is leaking urine during activities that put pressure on the bladder, such as coughing, sneezing, or laughing. In the case of urge incontinence, the main symptom is a sudden, strong urge to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine.
Other signs of urinary incontinence may include leaking urine when you cough, sneeze, or laugh; feeling a sudden, strong urge to pee; and needing to pee more often than usual. Being aware of these symptoms can help you identify the type of incontinence you may be experiencing and seek appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis and Tests

Diagnosing urinary incontinence typically involves physical exams, gathering your medical history, and keeping track of your bladder activity. Your healthcare provider may use urinalysis, bladder stress tests, pad tests, cystoscopy, urodynamic tests, pelvic exams, and measuring bladder pressures to determine the cause of your incontinence.You may be asked to keep a bladder diary, as well.
If the initial tests do not provide a clear diagnosis, your healthcare provider may recommend further testing, such as urodynamic testing. This can help identify any issues with bladder function and determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific type of incontinence.
Treatment Options

The treatment for urinary incontinence depends on the type and cause. Some possible options are home remedies, pelvic floor exercises, medications, medical devices, and surgery. Home remedies for urinary incontinence include urinary catheters and absorbent pads, which can provide temporary relief and help manage symptoms.
Pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegel exercises, can help strengthen the urinary sphincter and pelvic floor muscles, improving bladder control and reducing symptoms of urinary incontinence. Medications and medical devices, such as intermittent catheterization, can also be used to treat urinary incontinence by addressing the underlying cause.
In some cases, surgical treatments may be recommended to correct the issue and restore bladder function.
What is a Pelvic Health Physical Therapy?

Pelvic health physical therapy is a specialized form of physical therapy that focuses on strengthening the pelvic floor muscles to improve bladder control. This type of therapy uses manual "hands-on" therapy, therapeutic exercises, and other techniques to help strengthen and restore function to the muscles, nerves, and joints in the pelvic region.
The benefits of pelvic health physical therapy include enhanced bladder control, stronger pelvic floor muscles, better posture, and improved sexual function.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
There are several home remedies and lifestyle changes that can help manage urinary incontinence. Natural remedies like vitamin D, pumpkin seeds, soybean seed extract, saw palmetto, magnesium, capsaicin, ginger, and marshmallow root have been known to improve bladder function causing urinary incontinence. Additionally, lifestyle changes like losing weight, treating constipation, and cutting down on caffeine and alcohol can be helpful for improving urinary incontinence.
Absorbent products such as pads or protective underwear can also provide temporary relief and help manage urinary incontinence symptoms. These products are designed to absorb leaked urine and provide comfort and security, allowing you to continue with your daily activities without worry.
Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegels)
Kegel exercises are a type of pelvic floor exercise that can help strengthen the muscles responsible for bladder control. To perform Kegel exercises, contract and relax the muscles of your pelvic floor, as if you were trying to stop the flow of urine. Hold the contraction for 5 seconds, then relax for 5 seconds. Repeat this process 10 times to complete a set of Kegel exercises.
A doctor, nurse, or pelvic floor physical therapist can help you learn how to do Kegel exercises correctly and ensure you are targeting the right muscles. Regularly practicing Kegel exercises can help reduce the symptoms of urinary incontinence and improve your overall loss of bladder control.
Medications and Medical Devices
Various medications and medical devices can help treat urinary incontinence by addressing the underlying cause of the condition. These treatments may include drugs that relax the bladder muscles, reduce inflammation, or increase the tone of the urethral and sphincter muscles.
Medical devices, such as intermittent catheters, can help manage urinary incontinence by allowing the bladder to empty completely and preventing urine leakage. Catheterization may be required four to five times a day, with the goal of keeping the bladder volume at 15 ounces or less.
Catheter supply companies can deliver these devices discreetly through the mail, ensuring you have a consistent supply for effective management of your urinary incontinence.
Surgical Treatments
Surgical treatments for urinary incontinence may be recommended in cases where other treatments have not been successful. Surgical options include colposuspension, sling surgery, vaginal mesh surgery, urethral bulking agents, and artificial urinary sphincters.
For women with stress incontinence, the midurethral sling is the most common type of surgery used to correct the issue. This procedure involves placing a supportive sling around the urethra to help keep it closed during activities that put pressure on the bladder, preventing urine leakage.
Other surgical treatments, such as colposuspension or artificial urinary sphincters, may be recommended based on the specific type and cause of incontinence.
Prevention Strategies

There are several prevention strategies that can help reduce the risk of developing urinary incontinence or manage existing symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight is important, as excess weight can put pressure on the bladder and contribute to stress urinary incontinence often. Avoiding constipation can also help prevent urinary incontinence, as constipation can strain the pelvic floor muscles and exacerbate bladder control issues.
Regularly practicing pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegel exercises, can help strengthen the muscles responsible for bladder control and reduce the symptoms of urinary incontinence. By incorporating these prevention strategies into your daily routine, you can help maintain good bladder health and reduce your risk of developing urinary incontinence.
Seeking Professional Help

If you suspect that you may have urinary incontinence, it's essential to seek professional help to get an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. Consult a urologist, urogynecologist, or obstetrician for diagnosis and treatment of urinary incontinence. They can help identify the specific type of urinary incontinence treated you are experiencing and recommend the most suitable treatment options for your situation.
Don't be embarrassed to discuss your symptoms with a healthcare professional. Urinary incontinence is a common issue that affects millions of people worldwide. By seeking professional help, you can take the first step toward regaining control over your bladder and improving your quality of life.
Summary
In conclusion, urinary incontinence is a common and often treatable condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the different types of incontinence, their causes, and symptoms can help you identify the most suitable treatment options, ranging from home remedies to surgical interventions. By taking control of your bladder health and seeking professional help when needed, you can improve your quality of life and regain the confidence to live life without fear of unexpected urine leakage.
Everything You Need to Know About Incontinence But Were Afraid to Ask
All of our guides, downloads, worksheets, Premium courses
Click Subscribe To Get Started.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 types of incontinence?
Suffering from urinary incontinence? Know that you're not alone! There are four types of this condition: urgency incontinence, stress incontinence, functional incontinence and overflow incontinence.
Fortunately, there are many treatments available such as behavioral therapies, medications, nerve stimulation and surgery.
What is the main cause of incontinence?
The main cause of incontinence is weakened muscles and nerves in the bladder, as well as certain events unique to women like pregnancy, childbirth and menopause. Overweight or certain medications may also contribute to bladder control problems.
It's important to talk to your doctor to find the cause of your incontinence and get the right treatment.
How do I fix my incontinence?
To help fix your incontinence, try to limit caffeine and alcohol intake, do pelvic floor exercises (Kegels) regularly, void on a schedule, practice double voiding, and maintain a healthy weight.
By making these lifestyle changes, you may be able to reduce or stop your incontinence altogether.
What causes incontinence in females?
Females can suffer from incontinence due to issues with muscles and nerves which control the bladder. Unique health events like pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause can cause these muscles and nerves to be weakened or damaged.
Overweight is also a potential cause of female incontinence.
Why can't I hold my pee all of a sudden?
It sounds like you may be suffering from Urge Incontinence, which can cause an inability to hold your pee. With the help of your doctor, you can determine the best course of treatment to help manage your condition.
Our Resources section can help you find the information and tools that you need. We have courses, videos, checklists, guidebooks, cheat sheets, how-to guides and more.
You can get started by clicking on the link below. We know that taking care of a loved one is hard work, but with our help you can get the support that you need.
Click here to go to Resources Section now!





