Understanding Swallowing Difficulties: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Swallowing difficulties, or dysphagia, can significantly affect the quality of life. Swallowing is an important and complex process that can be disrupted, leading to serious health consequences.
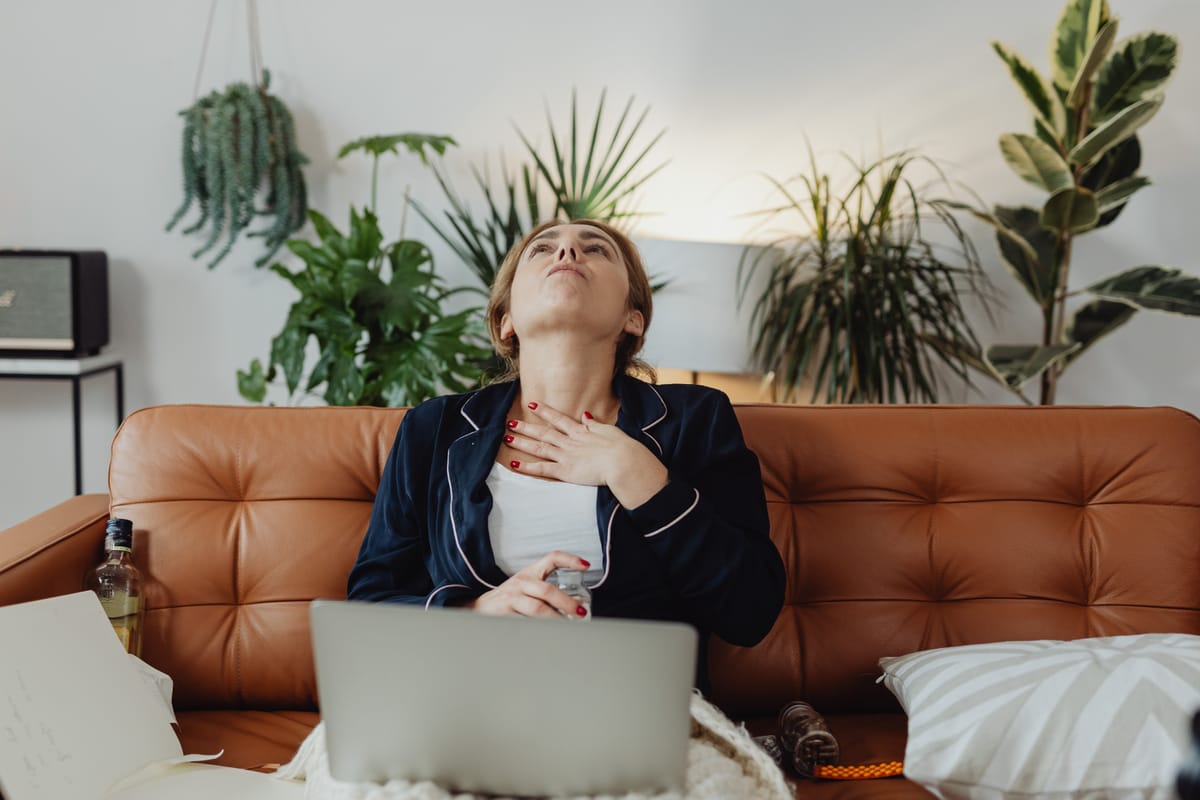

Did you know that swallowing is a complex process involving over 50 pairs of muscles and multiple nerves? For most people, swallowing is as natural as breathing. However, for some, swallowing difficulties, or dysphagia, can significantly affect their quality of life. In this blog post, we'll delve into the intricacies of a swallowing disorder, the symptoms and causes of swallowing difficulties, and the available treatment options to help those affected regain their ability to enjoy meals and maintain their health.
Short Summary
- Swallowing is an important and complex process that can be disrupted, leading to serious health consequences.
- Symptoms of swallowing difficulties include coughing, choking, pain in the throat and taking longer to eat.
- Treatments for swallowing difficulties involve medications, therapy exercises and diet changes. Feeding tubes may be necessary in severe cases.
Understanding Swallowing: The Process and Its Importance
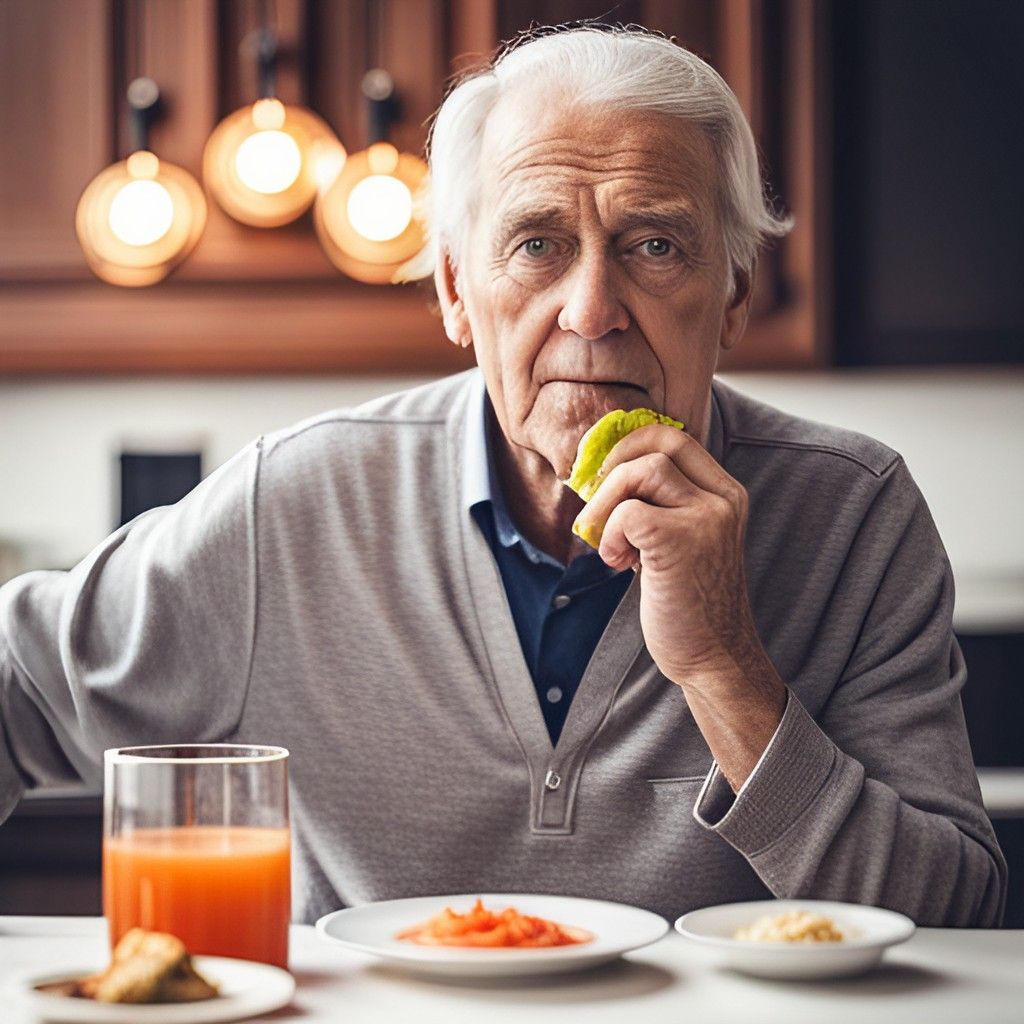

Swallowing is a complex process that requires seamless coordination between muscles and nerves. It plays a vital role in our everyday lives, allowing us to consume food and drink without choking or .
When this process is disrupted, it can cause difficulty swallowing, leading to malnutrition, dehydration, and even aspiration pneumonia – a serious lung infection. Swallowing difficulties are more common in older adults, but can affect people of all ages, especially those with certain neurological disorders or structural abnormalities.
The Three Stages of Swallowing
Swallowing occurs in three stages: oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal. In the oral stage, the tongue collects food or liquid, preparing it for swallowing. The tongue and jaw move solid food around the mouth to be chewed, breaking it down into the right size and texture for swallowing while mixing it with saliva.
During the pharyngeal stage, the food passes through the pharynx, or throat. The larynx (voice box) closes tightly, and breathing stops momentarily to ensure food or liquid doesn't enter the airway and lungs. This intricate dance of muscles and nerves is essential to prevent choking or aspiration.
The Role of Muscles and Nerves in Swallowing
Muscles and nerves work in harmony to move food or drink from the mouth to the stomach. Muscles located in the mouth, throat, and esophagus contract and relax in a coordinated manner, guided by nerves such as CN V3, IX, X, XII, the ansa cervicalis, and the recurrent laryngeal nerves.
When this delicate balance is disrupted due to neurological disorders, structural abnormalities, or other factors, swallowing difficulties can ensue. This highlights the importance of understanding the role of muscles and nerves in the swallowing process and seeking help when problems arise.
Common Symptoms of Swallowing Difficulties

If you or a loved one is experiencing swallowing difficulties, it's essential to recognize the warning signs and seek medical help when necessary. Common symptoms include coughing or choking while eating, pain when swallowing, and feeling like food is stuck in the throat.
In some cases, swallowing difficulties can also manifest as unexplained weight loss, dehydration, or taking longer to eat.
Identifying the Warning Signs

Besides the symptoms mentioned earlier, other warning signs of swallowing difficulties may include a hoarse voice after eating, drooling, problems swallowing and chewing food, and nasal regurgitation.
Addressing these signs promptly is crucial to prevent serious health complications such as malnutrition, dehydration, and aspiration pneumonia.
When to Seek Help
It's important to consult a physician if you're experiencing swallowing difficulties regularly or if they're accompanied by weight loss, regurgitation, or vomiting. If you have difficulty breathing or suspect something might be stuck in your throat, seek medical help immediately.
If you experience sudden muscle weakness or paralysis, resulting in an inability to swallow, call 911 or head immediately to the emergency room. Seek medical assistance without delay.
Causes of Swallowing Difficulties

There are several potential causes of swallowing difficulties, ranging from neurological disorders and structural abnormalities to allergies or inflammation.
Understanding the root cause of your swallowing difficulties is essential for determining the most effective treatment plan.
Neurological Disorders
Neurogenic dysphagia, or swallowing difficulties caused by problems with the nerves controlling the mouth, throat, and esophagus, can result from various neurological conditions. These include stroke, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
The impaired function of nerves in these disorders can lead to muscle weakness or poor coordination, causing swallowing difficulties.
Structural Abnormalities

Structural issues within the throat and esophagus can also contribute to swallowing difficulties. For example, narrowings or pockets in the esophagus can make it harder for food to pass through, leading to dysphagia.
Conditions such as achalasia, where the muscles in the esophagus become too stiff to let food and liquid pass into the stomach, can also cause swallowing problems.
Allergies and Inflammation

Allergies and inflammation can also lead to swallowing difficulties. Eosinophilic esophagitis, a chronic condition characterized by an allergic reaction to certain foods or environmental factors, can cause inflammation of the esophagus, making swallowing difficult.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, can also cause irritation and inflammation, contributing to swallowing difficulties.
Diagnosing Swallowing Difficulties
Accurate diagnosis of swallowing difficulties is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. Diagnosing these issues typically involves a combination of physical examinations and diagnostic tests to assess the function of the muscles and nerves involved in swallowing.
These tests can include imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans, as well as endoscopic examinations and manometry tests. The results were good.
Physical Examinations
Physical examinations for diagnosing swallowing difficulties include a patient history, physical examination, bedside swallow exam, and endoscopic examination.
These assessments can help healthcare professionals identify any abnormalities in the swallowing process and determine the most appropriate course of action to address the underlying issues.
Diagnostic Tests

Various diagnostic tests can be used to further assess swallowing difficulties, such as a bedside swallow test, water swallow test, manometry, modified barium swallow, esophagram, gastroesophageal endoscopy, and flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing (FEESST).
Videofluoroscopy, which uses X-rays to visualize the swallowing process, is considered the most reliable method for analyzing the oral and pharyngeal mechanisms of dysphagia.
Treatment Options for Swallowing Difficulties
Once swallowing difficulties have been properly diagnosed, various treatment options are available to address the underlying causes of swallowing problem and improve the individual's ability to swallow. These options include medications, swallowing retraining therapy, surgical interventions, diet modification, behavioral changes, and the use of thickening agents like Thick It.
Medications

Depending on the underlying cause of the swallowing difficulties, different medications may be prescribed to address the underlying issue. These can include prescription oral medications to reduce stomach acid, SSRIs, corticosteroids, antacids, PPIs, and muscle relaxants.
Consulting your physician is crucial for determining the most appropriate medication for your specific situation.
Swallowing Retraining Therapy
Swallowing retraining therapy, typically administered by a speech-language pathologist, focuses on retraining the muscles involved in swallowing and reducing the risk of choking and aspiration.
This therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals with dysphagia caused by neurological disorders or those who have undergone surgery affecting their throat muscles.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address swallowing difficulties. This can include the insertion of a stent, a metal mesh tube that opens up a passageway in the esophagus for food to pass through, or using botulinum toxin to temporarily paralyze tightened muscles, allowing food to reach the stomach more easily.
Diet Modification and Behavioral Changes

Modifying one's diet and implementing behavioral changes can significantly improve the ability to swallow and reduce the risk of aspiration pneumonia. These modifications can include altering the consistency of foods and liquids, adjusting eating habits and posture, and implementing bolus modification and management techniques.
Use of a Thickening Product
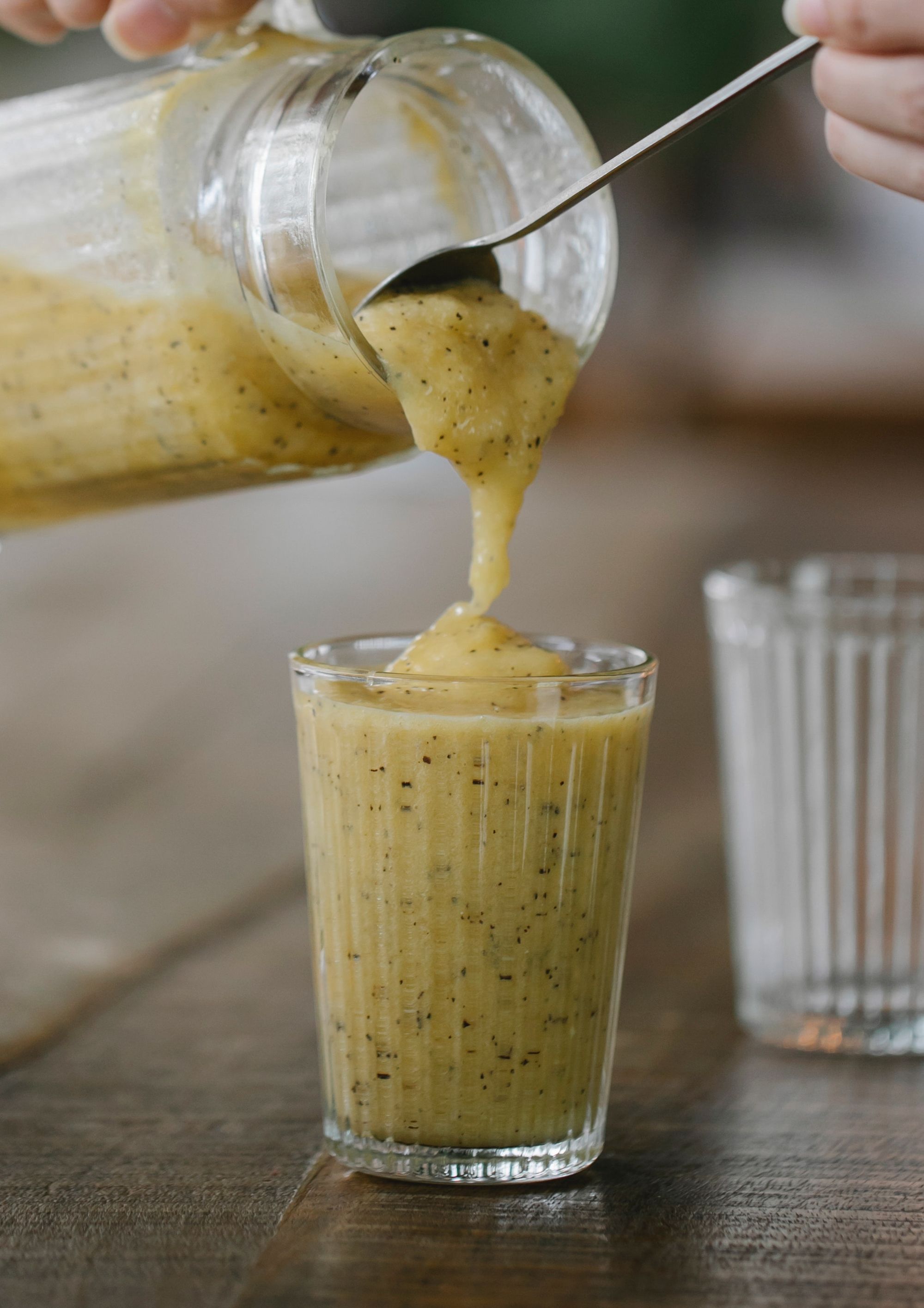

Helping your loved one stay hydrated and nourished can be a challenge, especially if they have difficulty swallowing. Don't limit meals to breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Instead, try smaller, more frequent meals, including healthy and hydrating snacks.
Thickened drinks can be an acquired taste, but they are crucial for hydration. If your loved one has trouble adjusting to the texture, try thickening fruit juices for a familiar flavor and texture. Keep in mind that thickened drinks may be less satisfying than regular beverages. Consider thickening their favorite drinks, like lemonade or iced tea.
Thickening agents can achieve a range of textures, from thin to spoon-thick. Talk to your loved one's doctor or speech-language pathologist to determine the best consistency for them. Natural thickeners like bananas and yogurt can also be added to meals. Pay close attention to dietary restrictions, such as allergies or diabetes, when choosing thickeners.
Don't worry - the selection of thickeners is constantly expanding. With a little creativity and care, you can help your loved one stay happy, healthy, and hydrated.
However, it's important to follow the instructions on the package and consult with a healthcare professional before using any thickening agents to ensure optimal results and safety.
Rehabilitation and Support for Swallowing Difficulties

Rehabilitation and support play a crucial role in managing swallowing difficulties and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Speech-language pathology and other swallowing therapy exercises are essential components of a comprehensive rehabilitation plan, helping to strengthen the muscles used in swallowing and teaching individuals safe swallowing techniques.
Speech-Language Pathology
Speech-language pathologists are trained healthcare professionals who specialize in diagnosing and treating communication and swallowing disorders. They can provide patients with swallowing difficulties with personalized exercises to strengthen the swallowing muscles and suggest safe swallowing techniques tailored to the individual's needs.
Swallowing Exercises
Swallowing exercises, such as tongue exercises, jaw exercises, and lip exercises, can help improve the function of the muscles involved in swallowing. By practicing these exercises consistently, individuals experiencing swallowing difficulties can gradually regain their ability to swallow safely and comfortably.
Feeding Tubes: When Are They Necessary?

In some cases, swallowing difficulties may be severe enough that a feeding tube becomes necessary to ensure adequate nutrition, prevent significant weight loss, and reduce the risk of choking. I have an article on Pros and Cons of Feeding Tubes in the Elderly Please take time to read it for more extensive information.
Understanding the different types of feeding tubes and when they might be needed can help individuals and their caregivers make informed decisions about their care.
Indications for Feeding Tube Use
Feeding tubes may be required when an individual is unable to obtain sufficient nutrition through regular eating and drinking due to severe swallowing difficulties, critical illness, or medical conditions that affect their ability to eat. Feeding tubes can also be used to prepare the bowel for surgery in very ill or malnourished patients or to address certain medical complications, such as enterocutaneous fistulas or small-bowel obstructions.
Types of Feeding Tubes
There are several types of feeding tubes, including nasogastric tubes, nasojejunal tubes, gastrostomy tubes (such as PEG tubes), and jejunostomy tubes. Nasogastric tubes are inserted through the nose and into the stomach, while nasojejunal tubes pass through the nose and into the small intestine.
Gastrostomy tubes, like PEG tubes, are inserted directly into the stomach through the abdominal wall, whereas jejunostomy tubes are placed directly into the small intestine.
Preventing and Managing Aspiration Pneumonia
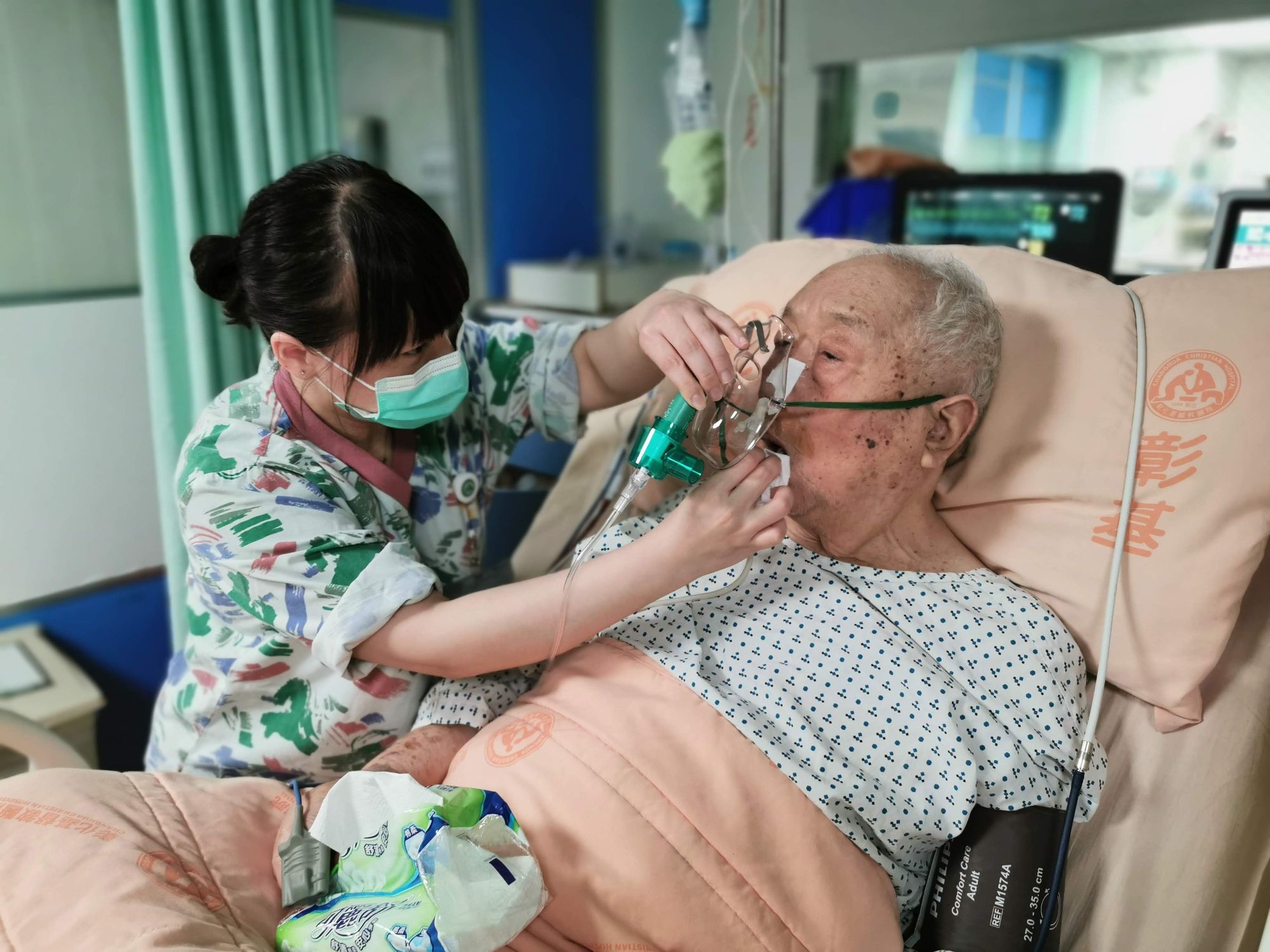

Aspiration pneumonia is a serious complication of swallowing difficulties, resulting from the accidental inhalation of food, saliva, vomit, or other substances into the lungs. This lung infection can be life-threatening, making the prevention and management of aspiration pneumonia a critical aspect of care for individuals with swallowing difficulties.
Understanding Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia occurs when food, liquid, or other substances enter the lungs instead of the stomach, causing an infection. It is a serious condition that often requires antibiotic treatment and can be life-threatening.
Individuals with swallowing difficulties are at an increased risk of developing aspiration pneumonia due to the impaired function of the muscles and nerves involved in the swallowing process.
Prevention Strategies

Preventing aspiration pneumonia in individuals with swallowing difficulties involves several strategies, including modifying the texture and consistency of foods and liquids, maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding distractions while eating, and implementing postural adjustments during meals.
By adopting these preventative measures, individuals with swallowing difficulties can significantly reduce their risk of developing aspiration pneumonia and improve their overall health and well-being.
Summary
In conclusion, swallowing difficulties, or dysphagia, can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and health. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and seeking appropriate treatment are essential steps in managing this condition. With the help of healthcare professionals, such as speech-language pathologists, and the implementation of various treatment options and preventative measures, individuals with swallowing difficulties can regain their ability to enjoy meals and maintain their health. Remember, seeking help early on can make a significant difference in your journey towards improved swallowing function and a better quality of life.
Our Resources section can help you find the information and tools that you need. We have courses, videos, checklists, guidebooks, cheat sheets, how-to guides and more.
You can get started by clicking on the link below. We know that taking care of a loved one is hard work, but with our help you can get the support that you need.
Click here to go to Resources Section now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 types of dysphagia?
Dysphagia is typically classified into four main types: oropharyngeal dysphagia, esophageal dysphagia, esophagogastric dysphagia, and paraesophageal dysphagia. Each of these types affects the various parts of the digestive tract differently.
Understanding the different types of dysphagia is key to proper diagnosis and treatment.
How do you relieve difficulty swallowing?
If you're having difficulty swallowing, talk to your doctor about treatments that may help. These might include speech and language therapy, changing the consistency of your food and liquids, using special utensils, taking medications to treat acid reflux, or opting for alternative forms of feeding like tube feeding.
Taking smaller, more frequent meals and chewing your food thoroughly can also help improve swallowing.
When should I be worried about trouble swallowing?
If you're having any difficulty swallowing or breathing, it's important to contact your doctor right away. You should also seek medical help immediately if something feels stuck in your throat or you experience sudden muscle weakness or paralysis.
Otherwise, it's a good idea to keep an eye on the issue and see a doctor if it persists.
What is Thick-It thickener used for?
Thick-It is a food and beverage thickener specifically designed for people with dysphagia. It helps to easily thicken liquids and pureed foods while decreasing the risk of choking and aspiration.
In other words, Thick-It makes it easier and safer for people with dysphagia to consume food and drinks.
What are the ingredients in Thick-It thickener?
Thick-It® products contain modified cornstarch, maltodextrin, xanthan gum, and ascorbic acid. Whether you choose Original or Clear Advantage®, you'll have all the ingredients you need to help thicken your favorite foods and drinks!
Thick-It® products are designed to help make mealtime easier for those with dysphagia. They provide a safe and easy way to thicken liquids and pureed foods to the desired consistency. With Thick-It®.
All of our guides, downloads, worksheets, Premium courses
Click Subscribe To Get Started.
You might also like this article:






