Feeding Tube Pros and Cons: A Comprehensive Guide for Caregivers
Discover the benefits and drawbacks of feeding tubes for elderly patients with this comprehensive guide.
As seniors age, swallowing food can become challenging, prompting discussions on enteral nutrition. Early consideration of this topic allows individuals to make informed decisions while they can. Having an Advanced Directive in place honors their wishes and eases decision-making for family members later on.
Opinions on enteral nutrition vary. Some prioritize quality of life and decline artificial nutrition, while others see feeding tubes as a means to prolong life. Nursing home residents often rely on feeding tubes, requiring increased care and monitoring.
An Advanced Directive does not hasten death, nor does hospice care. Enteral nutrition and intravenous feeding can extend the lives of older adults and critically ill patients.
Enteral nutrition involves providing liquid nutrition through a tube into the stomach or small intestine. However, it should be carefully considered as one of many therapies available. Liquid diets are often used with feeding tubes to ensure proper nutrition.

Peg Tubes and Enteral Feedings/Elderly Feeding Tube How Long LIve?
The duration of life with parenteral and enteral nutrition varies depending on individual health conditions. Some, like those with advanced dementia or progressive neurological disorders, may not benefit from extended life. For head and neck cancer patients, a peg tube can aid in nutrition during treatments, supporting healing and recovery.
Research suggests that enteral nutrition does not significantly impact life expectancy for most elderly individuals without additional medical interventions. It’s crucial to be informed about the pros and cons of feeding tubes and liquid nutrition for end-of-life planning, especially for those who haven’t made decisions in advance.
Feeding tubes can be an effective tool to help those who cannot eat or drink on their own. However, it is important to understand that oral supplements and enteral nutrition should not be used as a means of life prolongation in the elderly or those with terminal illnesses. It is important to discuss your individual needs and preferences for hand or tube feeding with your doctor, as well as consider the potential benefits of blenderized tube feeding or other blended diets. Ultimately, you have to decide what is best for you and your family.
Enteral feeding tubes play a crucial role in providing liquid nutrition to elderly patients who face challenges with swallowing or digestion. Several types of tubes, including gastrostomy tubes (G-tubes), jejunostomy tubes (J-tubes), and others, offer various benefits and drawbacks.
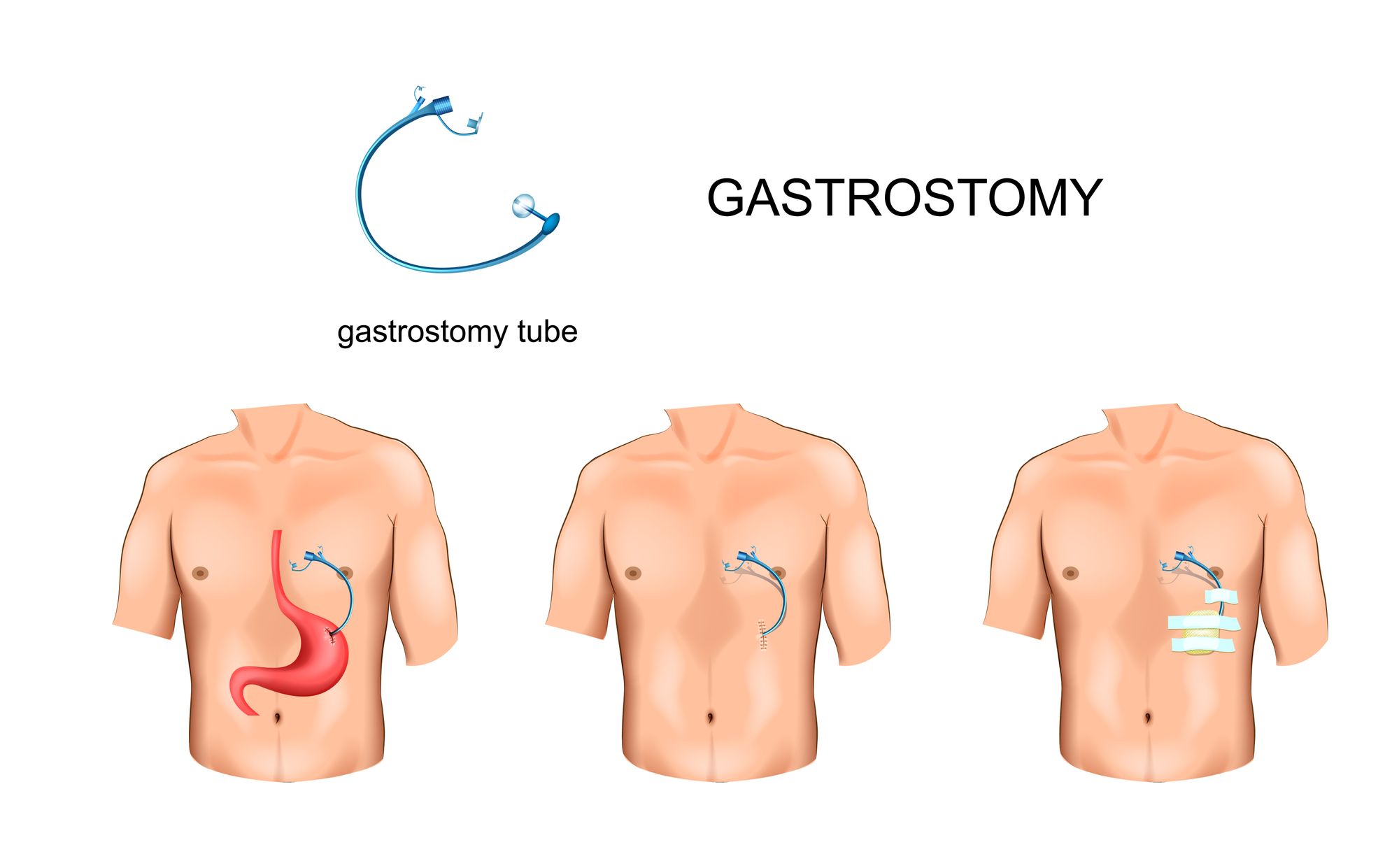
Feeding tube insertion through abdominal wall
Pros of Feeding Tubes:
· Provides essential nutrients and energy for those unable to swallow or digest food.
· Helps prevent malnutrition and reduces the need for hospitalization.
· Various tube types (e.g., gastrostomy, balloon peg, flying squirrel g tube) offer flexibility and options for individual needs.
· Some tubes can reduce infection rates and work in conjunction with other feeding methods.
· Enteral feeding pumps allow slow and consistent nutrient delivery.
Cons of Feeding Tubes:
· Invasive procedure with potential risks, such as infection and bleeding.
· Potential complications like aspiration pneumonia or edema due to mechanical feeding in the small intestine.
· Tube placement may require sedation for confused or agitated patients.
· Feeding tubes cannot replicate the pleasures of taste or social interaction during meals.
· Should not be used as a means of life prolongation for those with terminal illnesses.
Considerations for Feeding Tube Care:
· Frequent monitoring and tube placement checks are necessary to ensure effectiveness and safety.
· Professional training and guidance (e.g., PEG training courses) are vital for caregivers.
· Careful calculations for tube feeding amounts based on individual needs and preferences.
· Discuss with a doctor to determine the best type of tube feedings and consider blenderized food as an option. Ask for assistance in creating a care plan for peg tube feeding
Feeding tube Complications in the Elderly
Feeding Tube Complications in the Elderly/ Feeding pump
In conclusion, feeding tubes can be a valuable tool for elderly patients who cannot eat or drink independently. Similarly, feeding tubes are crucial for sick or injured cats who cannot eat independently due to illness or trauma. However, their use should be carefully evaluated based on individual needs and preferences. Feeding tubes should not be used as a means to prolong life for terminally ill patients. It is crucial to have open discussions with healthcare providers and consider all options before making decisions about feeding tubes. The focus should always be on providing the best care and comfort for the patient during their end-of-life journey.
Are feeding tubes dangerous?
Feeding tubes are generally considered safe when used correctly and monitored regularly. However, like all medical treatments, there are some risks associated with them. These include infection at the tube site, blockages due to food or medication build-up in the tube, and aspiration of food into the lungs. The use of an e tube, particularly for cats facing feeding challenges due to health issues, can also present potential complications such as tube dislodgement and irritation. It is important to discuss any potential risks with your doctor and healthcare team before beginning any form of enteral nutrition. Additionally, it is important to follow all instructions provided by your healthcare team for proper care and maintenance of the feeding tube in order to minimize the risk of complications.
Overall, while there are some risks associated with feeding tubes, they can provide important nutrition when oral feeding is not possible. It is important to discuss all potential risks and costs with your doctor before making any decisions about enteral nutrition. With careful monitoring and proper use, feeding tubes can be an effective method of nutritional support for many people.
Does the size of the tube determine how well a person will receive nutrition?
The size of the feeding tube does not necessarily determine how well a person receives nutrition. The size of the tube will depend on several factors, such as the type of nutrition being delivered and the patient’s individual needs. However, larger diameter tubes allow for feeding thicker food, which reduces the likelihood of clogs and complications during feeding. Additionally, it is possible for smaller tubes to deliver more nutrition than larger ones, as long as the flow rate is properly regulated. It is important to discuss all of these factors with your healthcare team before beginning enteral nutrition in order to make sure that you are receiving the proper amount of nourishment.

Percutaneous feeding tubes, Benefiber tube feedings
Are there any alternatives to feeding tubes?
Yes, there are other options for those who cannot receive adequate nutrition through traditional oral feeding. These include nasogastric (NG) tubes, gastrostomy tubes (G-tubes), and percutaneous feeding tubes, or endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes. Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages that will depend on the individual’s needs. It is important to discuss all alternatives with your healthcare team in order to find the best option for your nutritional needs.
A naso esophageal tube is another alternative for feeding, known for its ease of insertion under local anesthesia and suitability for short-term nutritional support.
Additionally, in some cases, nutrition can be delivered via a variety of alternative methods such as intravenous (IV) therapy or subcutaneous injection. Again, it is important to discuss all possible options with your doctor and healthcare team in order to make sure that you are receiving the proper amount of nourishment.
Are there benefits to a benefiber tube feeding?
Benefiber tube feedings can be a beneficial form of enteral nutrition for some individuals. It is important to discuss this option with your doctor and healthcare team as there are both advantages and disadvantages that come with it.
The main benefit of Benefiber tube feedings is that they provide a steady flow rate of carbohydrates, protein, fat, vitamins, minerals, and fiber that can help support nutrient intake. Additionally, this type of feeding can reduce the risk of clogs and blockages due to food residue in the tube. Finally, it is also easy to adjust the flow rate depending on individual needs.
Compared to syringe feeding, which can be stressful and challenging for both the patient and the caregiver, Benefiber tube feeding offers a more controlled and less stressful method of providing nutrition.
On the other hand, there are some drawbacks associated with Benefiber tube feedings. These include a slightly higher cost than other forms of enteral nutrition, as well as a slightly higher risk of aspiration due to the high fiber content in the formula. Additionally, it is important to note that Benefiber may not be suitable for everyone as some people may have difficulty digesting this type of formula.
It is important to discuss all options with your healthcare team before beginning any form of enteral nutrition in order to make sure that it is the right choice for you.
Overall, feeding tubes can be a beneficial form of nutritional support when oral feeding is not possible. It is important to discuss all potential risks and costs with your doctor before making any decisions about enteral nutrition. With careful monitoring and proper use, feeding tubes can be an effective way to ensure adequate nutrition for many individuals.
Your doctor and healthcare team can provide more information on the different types of feeding tubes, as well as alternative forms of enteral nutrition that may be suitable for your individual needs. They can also provide advice on how to best care for your tube in order to minimize risks and maximize benefits. It is important to always follow their instructions and recommendations when it comes to feeding tubes in order to ensure the best possible outcomes.
At the end of the day, it is important to remember that each person’s nutritional needs are unique. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any form of enteral nutrition in order to make sure that you get the right type of nourishment for your individual needs. With careful monitoring and proper use, feeding tubes can be a safe and effective way to ensure adequate nutrition for many individuals.
Do people with feeding tubes require any special care?
Yes, people who have undergone tube feedings may need some extra care depending on the type of feeding tube they have. For example, those with percutaneous feeding tubes may need to be monitored closely for any potential problems such as infection or leakage at the insertion site. Additionally, patients who have gastrostomy tubes will also likely need to take steps to protect the abdominal wall from potential damage due to prolonged use of a tube.
Proper care is equally important for pets with feeding tubes, and pet owners play a crucial role in ensuring their pets receive adequate care to improve outcomes.
It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and recommendations when it comes to caring for your tube in order to ensure the best possible outcomes. Additionally, it is important to always keep the area around the insertion site clean and dry and seek medical attention if any signs of infection or irritation occur. Regular follow-up visits with a healthcare professional are also recommended in order to monitor tube function and make sure that any necessary adjustments are made.
There are several complications that may occur. What should you do when a chest tube is accidentally pulled out?
If a chest tube is accidentally pulled out, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. In the meantime, pressure should be applied over the site from which the tube was removed in order to minimize any further bleeding or air leakage. Additionally, an X-ray may need to be taken in order to confirm that all parts of the tube have been successfully removed.
Most feeding tubes can be placed using standard equipment available in general practices, and only specific types, like PEG tubes, may require advanced techniques and training.
What about a g-tube balloon rupture?
G tube balloon rupture is a common complication of enteral nutrition and requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, or a decrease in the flow rate of the feeding. It is important to keep the area clean and dry and seek medical attention immediately if any signs of irritation occur. In the meantime, you can also reduce the amount of pressure in the balloon by adjusting the rate at which feedings are administered.
Feeding tubes are particularly crucial in post-operative care, especially after major surgery, to maintain nutrition in patients who have undergone significant surgical procedures.
Overall, it is important to always follow your doctor’s instructions when it comes to caring for your tube in order to ensure the best possible outcomes and minimize potential complications. With proper use and careful monitoring, feeding tubes can be an effective way to ensure adequate nutrition for many individuals.
What is the difference between nasoenteral feeding tubes,nasogastric feeding tubes and nasoenteric feeding tubes?
Nasoenteral feeding tubes, nasogastric feeding tubes and nasoenteric feeding tubes are all types of enteral nutrition which involve the insertion of a tube through either the nose or mouth. However, each type of tube has its own unique characteristics and benefits.
Nasoenteral tubes are typically inserted through the nose and make their way to the stomach. This type of tube is commonly used for patients who have difficulty swallowing or are unable to take oral nutrition due to medical conditions.
Nasogastric feeding tubes, on the other hand, are tubes that are inserted through the mouth and make their way directly to the stomach. These types of tubes are usually used for short-term nutrition support and might be recommended for those who have difficulty swallowing or need an alternative form of nutrition.
Finally, nasoenteric feeding tubes are tubes that are inserted through the nose and make their way directly to the small intestine. These types of tubes are generally used for long-term enteral nutrition support and can help provide adequate nourishment during extended periods of time. Additionally, this type of tube can help reduce the risk of aspiration since it bypasses the stomach and goes directly to the small intestine.
Esophagostomy (E) tubes are another type of feeding tube that is inserted through the neck into the esophagus. This procedure requires sedation and the tube functions by providing direct access to the esophagus for nutrition delivery.
Overall, each type of enteral feeding tube has its own set of benefits and drawbacks that should be carefully considered before beginning any form of nutritional support. It is important to discuss all available options with your healthcare provider in order to make sure that it is the right choice for you. With proper use and careful monitoring, these tubes can provide adequate nutrition for many individuals in need.
It is also important to note that patients who are considering tube feedings should always follow their doctor’s instructions regarding care and maintenance of the feeding tube in order to minimize potential complications and ensure its longevity. Additionally, regular check-ups and monitoring are essential in order to ensure that the tube is functioning properly and providing adequate nutrition. By taking all necessary precautions and following your doctor’s advice, tube feeding can be a safe and effective form of nutrition for many individuals.
What are nasojejunal feeding tubes?
Nasojejunal feeding tubes are a type of enteral feeding tube which is inserted through the nose and makes its way directly to the small intestine. They are commonly used for long-term nutritional support in patients who require an alternative form of nutrition due to medical conditions. Caring for a sick cat with feeding difficulties can be particularly challenging, and it is crucial to seek veterinary assistance to ensure proper care and improve recovery chances. These types of tubes help reduce the risk of aspiration since they bypass the stomach and go directly to the small intestine. Additionally, they provide a more direct form of nutrition for those who require it and can help ensure adequate nourishment during extended periods of time.
What are drainage gastrostomy tubes?
Drainage gastrostomy tubes (G-tubes) are a type of feeding tube that is inserted through the abdomen and into the stomach. These tubes are commonly used for those who require a long-term form of enteral nutrition or when oral feeding is not possible due to medical conditions. G-tubes provide an alternative form of nourishment and help reduce the risk of aspiration since all liquids go directly into the stomach rather than passing through the esophagus. Additionally, these types of tubes
Here are 2 PDf's on tube feedings from a doctor's perspective :
American Geriatrics Positions on feeding tubes for advanced dementia.
Ethical Issues with long term feeding tubes
More on G Tubes, Peg Tubes and Button G Tube
When it comes to elderly care, a feeding tube can be an important tool for ensuring that seniors are properly and safely nourished. However, there are both pros and cons of using such tubes that should be considered before making a decision.
One key benefit of feeding tubes is that they provide elderly individuals with necessary nutrition when they cannot eat or swallow on their own. Known as a gtube, or gastrostomy tube, this type of tube is inserted directly into the stomach through a small incision in the abdomen. It can provide seniors with nutrition that may otherwise be difficult for them to obtain, and it can also be used to deliver medication orally.
Gastrostomy Tube Care For Adults
However, there are some drawbacks to using feeding tubes in elderly individuals. For one, it is an invasive procedure that can be painful, and there are certain risks associated with it. Additionally, the costs of inserting and maintaining a feeding tube may not always be covered by Medicare or other insurance plans. And finally, in many cases, seniors may feel uncomfortable or embarrassed about using a feeding tube, which can have an effect on their overall quality of life.
Additionally, it is important to understand the types of feedings that can be administered through a feeding tube. Elemental formulas and other nutrient-dense liquids are typically used, and these require a cpt code for enteral feeding. The tube should also be placed in the correct site on the body to ensure proper nutrition delivery. With all this in mind, you should be able to make an informed decision about whether a feeding tube is right for the elderly individual in your care.
Ultimately, it's important to consider all the pros and cons of feeding tubes in elderly individuals before making a decision. You should carefully weigh the potential risks and benefits, discuss your options with medical professionals, and consult with family members or other caregivers

Frequently Asked Questions About Enteral Nutrition Include:
Can LPNs( licensed Professional Nurse) do enteral feedings?
Yes. Bolus tube feeding is a skill that even lay people (non-medical people) can do. Giving tube feedings is within all LPNs' scope of practice. It is not like IV therapy, which is limited in some states and wide open in others.
What happens if a G-tube is pulled out?
If your gastrostomy tube is accidentally removed or falls out, there's no need to panic. Just remember to note down the time. It's important to get a new feeding tube inserted as soon as possible to prevent the stoma tract (the hole in your skin) from closing completely within a few hours.
Here's what you should do next:
If you have a PEG tube (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube): If your PEG tube has been pulled out, it's necessary to go to the hospital for assessment and tube replacement to avoid complications. Cover the stoma tract with a dressing and bring your spare tube, if you have one, along with any information about your tube.
If you have a balloon gastrostomy tube (BGT) or low-profile balloon gastrostomy (LPBG or button): If the balloon is inflated and causing pain, you need to go to the hospital to have your tube replaced and be assessed for any complications. Cover the stoma tract with a dressing, bring your spare tube (if available), and any information about your tube. If the balloon is deflated and it's your first tube in that stoma tract or the tract is less than eight weeks old, it's important to go to the hospital for assessment and tube replacement. Cover the stoma tract with a dressing, bring your spare soft tube (if available), and any information about your tube.
If the balloon is deflated and it is not the first tube in that stoma tract and the tract is more than eight weeks old, you have a couple of options: You can temporarily maintain your stoma tract and prevent it from closing by following the instructions below if you feel comfortable doing so. Alternatively, you can contact your nurse and inform them about what happened, asking for an urgent tube replacement. If you or a caregiver have been trained, you can also replace the tube yourself.
Temporary maintenance of your gastrostomy stoma tract:
Sometimes, it may be possible or necessary to insert a new tube into the stoma tract without using it for flushing, feeding, or medication. This may be the case if: You or your caregiver are in the process of learning the entire tube replacement procedure and feel confident in placing the tube but not using it yet. A healthcare professional has advised you that it's more important to prevent the stoma from closing than to use the tube.
In such circumstances, gently place the replacement tube into your stoma tract, without applying any force. Stop if you experience any pain and seek medical attention. Secure the tube to your skin with tape. Remember not to use the tube for flushing, medication, or feeding. Contact the person responsible for replacing your tube or, when possible, go to the hospital to have a healthcare professional guide you through the next steps.
Important: If you have a stoma stopper like Enplug, you can use that instead to keep your stoma open.

Nurse discussing care plan for PEG tube feeding and tube feeding formula
Should certified nursing assistants (CNAs) be allowed to administer enteral feedings?
No, only nurses should do tube feedings. This requires accurate nursing assessment skills that nurses are taught.
Are tube feeds really beneficial for those with dementia or neurological conditions? Do they improve the quality of life?
Research isn't quite convinced.
Here are some risks associated with tube feeding in elderly patients with advanced dementia or progressive neurological conditions:
No evidence to suggest that tube feeding prevents aspiration risk, heals pressure ulcers, improves nutritional or cognitive status, or decreases mortality. Increased risk of recurrent and new-onset aspiration, infections related to tube feeds, increased oral secretions, and tube malfunction. Tube feeds can cause agitation and discomfort, leading patients to try to pull at their tubes. Just because a patient receives nutrition through a tube feed doesn't guarantee weight gain or a better quality of life.
The American Geriatric Society guidelines state that hand feeding can be just as beneficial as tube feeding. Research has found little to no benefit in prolonging end of life when using tube feeds for patients with advanced dementia compared to eating orally.
Can unlicensed assistive personnel administer enteral feedings?
The answer to these questions depends on each individual case. Generally, licensed professionals such as registered nurses and licensed practical nurses are the only ones authorized to administer enteral nutrition. Certified nursing assistants may be able to assist with set up and monitoring of a person's feeding schedule, but should not be the ones to actually administer the feedings. In terms of G-tubes, if one is pulled out then medical attention should be sought immediately.
Additionally, family members and caregivers should be educated on the proper care of enteral feeding tubes and how to administer IV push medications if needed.
Each of these questions should be discussed with a medical professional before any decisions are made. Ultimately, it is important to carefully consider the pros and cons associated with enteral nutrition so that an informed decision can be made.
What is a Nasogastric Tube Feeding?
Are you dealing with swallowing disorders or recovering from surgery? Consider using Dobhoff feeding tubes to maintain necessary nutrition without the risk of vomiting or aspiration. These nasogastric tubes are inserted through the nose and secured to prevent slipping into the lungs.
Dobhoff feeding tubes are versatile and can deliver medicine, fluids, vitamins, and food. While typically temporary, some individuals with swallowing disorders may require them for an extended period or permanently.
You can trust a healthcare professional, usually a nurse, to properly place your Dobhoff feeding tube. They will measure and mark the tube to ensure correct positioning in the stomach. A sample of stomach fluid will be taken to confirm proper placement. There is a protocol for a dobhoff bridle placement (ng tube) documentation nursing notes and the nursing interventions performed.
Taking care of your nasogastric feeding tube is essential. Remember to wash your hands before cleaning and administering fluids. Regularly check for redness, swelling, or sores around the nostrils. If you encounter any issues, seek medical assistance immediately. Make sure there is an ng tube syringe in the feeding set tubing kit. Flushing the tube with water every 8 hours will help prevent blockages.
Be mindful of any changes in the position of the tube or if fluids are not passing through it. These may indicate a problem and require medical attention. Fortunately, a healthcare professional may be able to clear the blockage without needing to replace the tube.
Fluoroscopic guidance is used to insert some tubes
Does Medicaid Pay for Tube Feeding?
Medicaid may cover the cost of tube feedings if it is deemed medically necessary and prescribed by a healthcare professional. It is important to check with your specific state's Medicaid program for coverage guidelines and requirements. In some cases, private insurance may also cover the cost of tube feedings. It is best to consult with your insurance provider for more information on coverage options.
Enteral Nutrition: Understanding Coverage Policies
Getting the right coverage for specialized nutrition can sometimes be confusing.
Let's break it down:
Medicare coverage:
Medicare Part B covers enteral nutrition (EN) when it's administered via a feeding tube. This coverage is available for beneficiaries at home, in a skilled nursing facility, or in a nursing facility not covered by Medicare Part A. EN is eligible for coverage under Medicare Part B if there is a permanent impairment that requires feeding via a tube. Examples include head and neck cancer with reconstructive surgery and central nervous system disease causing severe indigestion problems that cannot be managed with oral feeding.
Oral supplements:
Orally administered enteral supplements are not covered under Medicare Part B. However, they may be covered under certain state Medicaid programs or commercial insurance programs.
Potential limitations:
Some Medicaid and commercial payers use Medicare coverage policies to set their own coverage policies. This means that access to enteral products that are not required due to a permanent impairment or administered orally may be limited.
Varying coverage policies:
Coverage policies for enteral nutrition can vary across different payers and plans, adding to the complexity. Unfortunately, the uncertainty and complexity of a beneficiary's coverage can negatively impact their access to these important nutrition products.
Understanding these coverage policies is essential for ensuring access to the enteral nutrition that individuals need.
What is the difference between Osmolite vs Nutren?
Osmolite is a high calorie, high protein liquid diet designed to provide optimal nutrition for those who require enteral feedings. This type of formula typically contains carbohydrates, proteins and fats. It can also be used as a supplement to oral diets in order to help meet the patient's nutritional needs. Nutren is a specialized enteral formula with an osmolality similar to that of human milk. It contains added vitamins and minerals as well as probiotics and prebiotics for digestive support. Both of these formulas can be used in conjunction with other forms of nutrition therapy, including oral diets, tube feedings and intravenous (IV) nutrition.
What are the Three Buttons on a Peg Tube?
The three buttons on a peg tube refer to the way in which it is controlled. The first button is used to release medication or feedings, while the second and third buttons are used to control the rate at which they are released. This allows for accurate dosing of medications and nutrition based on the patient's individual needs. Additionally, the three buttons can be used to flush out any blockages that may occur in the tube or to help control the rate of flow for certain feedings. It is important to consult with a medical professional before using these buttons.
What are the Disadvantages of Peg Tube Feedings
Though there are many benefits to enteral feedings, it is important to consider the potential risks associated with them. Complications can occur such as infection ( increased bacteria count) at the tube site, aspiration of food into the lungs, or blockages in the tube due to food or medication build-up . Additionally, long-term use of a peg tube may lead to weakened muscles due to lack of use or increased risk of skin breakdown at the site where the tube enters the body. It is important to discuss all potential risks with your doctor and healthcare team before beginning any form of enteral nutrition.
It is also important to consider the financial costs associated with peg tube feedings. The amount that is covered by insurance can vary greatly depending on the type of plan and the specific services that are needed. Additionally, supplies such as feeding bags, tubing, syringes and other related materials will need to be purchased in order to maintain the tube. It is important to understand all of these costs before making any decisions about enteral nutrition.
Overall, there are many pros and cons associated with peg tube feedings. While they can provide important nutrition in cases where traditional oral feeding is not possible, it is important to consider the risks associated with them and be aware of all costs involved. It is best to discuss this option with your healthcare team before making any decisions about treatment.
How does a Nasal Bridle Work? ( a bridled ng tube)
A nasal bridle is a device that can be used to provide enteral nutrition when other methods are not an option. The device consists of a tube with two loops, one loop goes around each ear and the other end of the tube connects to a feeding bag or pump. This allows for controlled delivery of feedings through the nose instead of through the mouth. The nasal bridle is a safe and reliable option for those who are unable to take feedings orally. It is important to consult with a medical professional before using this method in order to ensure that the patient will be able to tolerate it safely. Additionally, it is important to monitor fluid intake and output closely in order to avoid any potential complications associated with enteral nutrition.
Finally, it is important to understand that the nasal bridle must be removed periodically in order to avoid infection and other complications associated with long-term use. It is best to consult with a medical professional for instructions on how often this should be done and how best to ensure safety during the process. Additionally, because of the location of the tube, proper hygiene practices should be taken to reduce the risk of infection.
How Do You Safely Remove an NG Tube?
When it is time to remove a nasogastric (NG) tube, there are certain steps that need to be followed in order to ensure safety and proper hygiene during the process. The first step is to NG tube removal is to gather all necessary supplies such as gloves, sterile gauze and clean towels. Next, the patient should be placed in a comfortable position either sitting up or lying down depending on their preference. The tube should then be slowly pulled out of the nose while gentle pressure is applied to the area around it. After the tube has been removed, it should be cleaned with alcohol swabs and disposed of properly according to your healthcare provider's instructions. Finally, the area should be cleaned and dressed with sterile gauze as needed.
It is important to remember that removing an NG tube can be a difficult process for some patients and it may take several attempts before it can be successfully removed. Additionally, it is important to ensure that the patient has adequate pain relief during the procedure in order to make it as comfortable as possible. It is best to consult with a medical professional before attempting to remove an NG tube in order to ensure the safety of all involved.
What is a Hot Tub for Enteral Feedings?
A hot tub for enteral feedings is a specialized device that allows for continuous delivery of nutrition and medication. This type of device works by using water to maintain a steady flow rate of both nutrients and medications. The hot tub also helps reduce the risk of tube clogs, which can be a common occurrence when using other types of feeding tubes. Additionally, the hot tub can be used to regulate temperature and ensure that the food or medication is kept at a safe temperature when being delivered. Finally, this type of device is also helpful for increasing patient comfort when receiving enteral feedings as it helps reduce the risk of discomfort from cold liquid entering the body.
Enteral nutrition is a life sustaining approach to care It will not cure teh condition
What are the Benefits of Creating Hot Tubs for Tube Feedings?
Creating hot tubs for enteral nutrition can provide many benefits for those who are receiving the feedings. One of the main benefits is that it can help to reduce pain and discomfort associated with the tube insertion. Additionally, hot tubs can help to improve digestion of enteral formula by allowing for increased blood flow and better absorption. Hot tubs also provide the patient with a more comfortable environment where they can relax while taking their feedings.
Creating a hot tub for tube feedings should be discussed with your healthcare provider before the process is started in order to ensure optimal safety and effectiveness. Additionally, it is important to monitor the patient's temperature closely to avoid any potential complications associated with overheating or dehydration. Finally, the patient should be monitored carefully while taking their feedings in order to ensure that the tube is properly positioned and functioning correctly. By following these precautions, hot tubs can be a great way to provide enteral nutrition in a safe and comfortable environment.
By understanding the pros and cons of enteral feedings, you can make an informed decision about what type of nutrition is best for your individual needs. It is important to discuss all potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider before starting any form of enteral nutrition. Additionally, it is important to be aware of the financial costs associated with this method as well as any supplies that may need to be purchased over time. By taking all of these factors into consideration, you can ensure that you are making an informed decision about your nutritional needs.
Where can I find more information about enteral nutrition?
The American Dietetic Association provides a wealth of information and resources on enteral nutrition. Additionally, there are several support groups such as the Continental Avenue Health Initiative in Brooklyn, NY that can provide further assistance to those who need help with their nutritional needs. It is important to remember that each person's individual needs should be taken into consideration when making decisions about which form of nutrition therapy is best for them. Consulting with a medical professional is the best way to ensure that the right decision is made.
Can a PCA give a tubal feeding?
Yes, a PCA (professional care attendant) can give tubal feeding. However, the caregiver must be trained to insert and maintain the tube as well as ensure that the patient is receiving an adequate amount of nutrition. It is important to follow all instructions from your healthcare team in order to make sure that the tube is inserted properly and functioning correctly. Additionally, regular check-ups and monitoring should be done to ensure that the tube is providing the necessary nutrition and there are no potential complications. Furthermore, it is essential to have a backup plan in place in case something goes wrong with the tubes or if other nutritional needs arise. By following all instructions given by your healthcare team, a pca can safely and effectively provide tubal feeding for those who require it.
Finally, blended diet for tube feeding recipes can be used to add additional nutrition and variety for one's daily meals. These recipes allow individuals to enjoy a wide range of healthy meals while still receiving the necessary nutrition from their tubes. The recipes can be as simple or as complex as desired and can be tailored to fit any dietary restrictions or needs that may be in place. By utilizing these blended diet recipes, individuals can enjoy delicious meals while still receiving adequate nourishment from their tubes.
Overall, tube feedings can provide a safe and effective form of nutrition for those who require it. It is important to carefully consider all options before beginning any form of nutritional support and have a backup plan in place if necessary. Additionally, it is essential to follow all instructions from your healthcare team in order to ensure that the tube is inserted correctly and providing adequate nourishment. With the right care and maintenance, tube feedings can be a beneficial form of nutrition for many individuals.
By incorporating blended diet for tube feeding recipes, individuals can enjoy variety and flavor while still receiving their necessary nutrients through their tubes. This allows for a more enjoyable eating experience while still providing the necessary nutrition needed to stay healthy. By combining these recipes with proper care and maintenance, individuals can enjoy nourishing meals and receive the necessary nutrition from their tube feedings. With the right combination of tube feeding and dietary choices, individuals can live healthier lives and receive adequate nourishment.
What is the process for a peg tube insertion?
PEG (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy) tube insertion is a common surgical procedure used to insert enteral feeding tubes directly into the stomach. The procedure is typically performed in an operating room under general anesthesia and requires the use of an endoscope to guide the placement of this flexible tube. Once in place, the tube can be secured with sutures or a balloon to ensure that it remains in position. Additionally, the tube can be used for feeding, medications, or drainage purposes.
The insertion of a PEG tube is typically safe and requires minimal recovery time. However, as with any surgical procedure there are risks involved and it is important to discuss all potential complications with your healthcare team before proceeding. It is also essential to follow all instructions from your healthcare team in order to ensure the proper care and maintenance of the tube. With adequate preparation and careful monitoring, PEG tube insertions can be a safe and effective way to provide enteral nutrition for those who require it.

Feeding tubes in the elderly
What Tube is Used in Some Operations?
The tube that is used in some operations, such as PEG tube insertion, is called a gastrostomy tube. This tube is inserted directly into the stomach through a small incision in the abdomen and can be used for feeding or drainage purposes. Other types of tubes, such as nasojejunal or G-tubes, may also be used in certain operations depending on individual needs.
What are some common CPT codes associated with tube feedings?
The most commonly used CPT codes for tube feedings are 43760, which is used for the insertion of a gastrostomy tube, and 74230, which is used for fluoroscopic guidance during the procedure. Other CPT codes may be used depending on specific circumstances and individual needs.
How can I get coram feeding supplies?
Coram, a leading provider of home infusion and tube feeding services, can be contacted directly for ordering supplies. They can be reached at 1-800-718-5031 or through their website. Additionally, your healthcare team may also have information on how to obtain coram feeding supplies.
Can I receive tube feedings at home?
Yes, it is possible to receive tube feedings at home with proper education and support from healthcare professionals. This can provide a more comfortable and convenient environment for tube feedings, as well as allow for greater independence for individuals who require them. However, it is important to regularly monitor the tube and follow all instructions for care and maintenance in order to prevent any complications.
Are you or a loved one receiving tube feedings through a gastrostomy (G-tube) and experiencing skin irritation?
We understand how frustrating and uncomfortable this can be. That's why we've compiled some frequently asked questions about G-tubes and barrier creams to help alleviate your concerns.
What is the best barrier cream for G-tubes?
There are several options for barrier creams that can help protect the skin around a G-tube. Some popular choices include Cavilon Durable Barrier Cream, Coloplast Brava Protective Barrier Cream, and Medline Remedy Skin Repair Barrier Cream. It is important to discuss with your healthcare team which option would be most suitable for you based on your individual needs.
How often should I check my G-tube placement?
It is recommended to check the placement of your G-tube at least once a day, or as directed by your healthcare team. This can help prevent complications and ensure proper nutrition delivery.
What is the cost of tube feeding per day?
The cost of tube feeding per day can vary depending on individual needs and factors such as type of formula used and supplies required. It is best to discuss this with your healthcare team or insurance provider for a better estimate.
How can I minimize skin exposure to tube feedings?
One way to minimize skin exposure to tube feedings is by using a dressing or protective cover around the G-tube site. This can help prevent leakage and excess moisture from causing skin irritation.
What is granulation tissue and how can it be managed?
Granulation tissue is a common complication of G-tubes where excess pink or red tissue forms around the site. It can cause discomfort and may lead to infection if not properly managed. Using a protective barrier cream and keeping the area clean and dry can help manage granulation tissue.
What is the best skin protectant for G-tube site?
There are several options for skin protectants, such as silicone-based creams or sprays, that can help create a barrier between the G-tube and the skin. It is important to consult with your healthcare team for recommendations on which option would be most suitable based on your specific needs.
By using a high-quality barrier cream and taking proper precautions, you can minimize the risk of skin irritation and discomfort while receiving tube feedings through a G-tube.
Remember to consult with your healthcare team for personalized advice and support. We hope this information has been helpful in addressing some common concerns about G-tubes and their associated skin care. So, don't hesitate to ask for help when needed in order to ensure the best possible care for yourself or your loved one. Remember, proper skin care is essential for overall health and well-being.
How can I prevent my feeding tube from getting clogged?
- The best way to prevent clogging is by flushing the tube with warm water before and after each use. Additionally, ensuring that the formula is at room temperature can also help prevent clogs.
What should I do if my feeding tube becomes clogged?
If your feeding tube becomes clogged, try gently massaging the tube or using a specialized unclogging device. If these methods do not work, contact your healthcare team for further instructions.
What is the difference between a Dobhoff tube and a Corpak tube?
A Dobhoff tube is a small bore feeding tube that is inserted through the nose and into the stomach, while a Corpak tube is inserted directly through the skin into the stomach. Both serve the same purpose of delivering nutrition, but the method of insertion may vary based on individual needs and circumstances.
Is there a website where I can learn more about enteral therapy?
Yes, enteraltherapy.com is a helpful resource for learning more about tube feedings and other forms of enteral therapy.
How do bridles help with feeding tubes?
Bridles are a type of securing device that can be used to prevent feeding tubes from being dislodged or pulled out accidentally. They are typically used for nasal feeding tubes, such as the Dobhoff tube.
Can I use jevity 1.5 as an equivalent to my current tube feeding formula?
It is important to consult with your healthcare team before switching formulas, as they can advise on the best option for your specific nutritional needs. Jevity 1.5 is a high-protein, high-calorie formula that may be suitable for some individuals but not others.
What is the medical meaning of a "cat" feeding tube?
A cat feeding tube, also known as a small bore feeding tube, is a thin tube typically inserted through the nose and into the stomach for administering nutrition to patients who are unable to consume food orally. It is named after its size, which is similar to the diameter of a cat's whisker.
How often should I check my G-tube placement?
It is recommended to check G-tube placement daily before each feeding, to ensure it has not moved or become dislodged. If you notice any changes in the tube's position, contact your healthcare team for further instructions.
Is warm water the only way to unclog a feeding tube?
Warm water is a safe and effective method for unclogging feeding tubes, but there are also specialized tools available that can help when warm water alone does not work. It is important to consult with your healthcare team for personalized recommendations on how to unclog your specific feeding tube.
Are there any other tips for preventing clogs in my feeding tube?
In addition to flushing the tube with warm water and keeping formula at room temperature, it is also recommended to avoid using medications or supplements through the feeding tube unless approved by your healthcare team. These can contribute to clogging of the tube.
Keep these tips in mind when caring for a feeding tube in the elderly and always consult with your healthcare team for personalized advice and support. Remember, taking care of yourself or a loved one goes beyond just physical health – it also includes promoting comfort and well-being. Keep up the great work!
What is a PEG tube, and how does it work for elderly patients?
A PEG tube, or Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy tube, is a medical device that provides a way to deliver nutrition directly to the stomach through a small incision in the abdominal wall. It is often used in elderly patients who have difficulty swallowing or consuming food orally. A PEG tube is inserted through the skin and into the stomach, allowing for enteral nutrition, which is the delivery of nutrients through the gastrointestinal tract.
What are the pros of using a PEG tube for elderly patients?
There are several advantages to using a PEG tube in elderly patients:
- Nutritional Support: PEG tubes ensure that elderly individuals receive adequate nutrition when they are unable to eat or drink orally.
- Medication Administration: Medications can be easily administered through the PEG tube, making it a convenient option for patients with multiple medications.
- Reduced Aspiration Risk: Using a PEG tube reduces the risk of aspiration pneumonia, a common concern in elderly patients with swallowing difficulties.
- Improved Quality of Life: By providing adequate nutrition and reducing discomfort during eating, PEG tubes can improve the overall quality of life for elderly patients.
Are there any cons or potential drawbacks to using PEG tubes in the elderly?
Yes, there are some disadvantages and considerations:
- Invasive Procedure: The insertion of a PEG tube is a medical procedure that carries some risks, including infection or complications during the placement.
- Loss of Oral Enjoyment: Using a PEG tube means losing the pleasure and social aspects of eating, which can impact an elderly patient's emotional well-being.
- Maintenance and Care: PEG tubes require proper maintenance, and caregivers must ensure that they remain clean and functional.
- Pain or Discomfort: Some elderly patients may experience discomfort or pain at the insertion site.
- Ethical and End-of-Life Considerations: Decisions regarding PEG tube placement should consider an individual's preferences, goals of care, and potential end-of-life choices.
What is the difference between enteral feeding and total parenteral nutrition (TPN)?
Enteral feeding is the delivery of nutrition through the gastrointestinal tract, such as via a PEG tube, allowing the body to process nutrients naturally. Total parenteral nutrition (TPN), on the other hand, is the intravenous administration of all nutrients, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract. TPN is typically used when the GI tract cannot absorb nutrients, while enteral feeding remains the preferred method when possible.
Can you explain the role of a nutrition support team in managing enteral and parenteral nutrition for the elderly?
A nutrition support team plays a crucial role in evaluating and managing the nutritional needs of elderly patients. They assess whether enteral nutrition, such as through a PEG tube, or parenteral nutrition is appropriate. The team also monitors patients, adjusts feeding regimens, and provides guidance on nutrition-related issues.
Is there any technology or tools available to assist with managing enteral feeding in the elderly?
Yes, there are tools and technologies available to assist with enteral feeding:
- Feeding Pump Calculator App: There are mobile applications that help calculate the appropriate feeding rates for PEG tubes, ensuring precise nutrient delivery.
- Free Water Flush Calculator: This tool helps determine the appropriate amount of water needed to flush PEG tubes and maintain their patency.
- Remote Proctoring for Enteral Nutrition Exams: Remote proctored exams for enteral nutrition courses and certifications allow professionals to learn and get certified in this specialized field from the comfort of their own locations.
What is the difference between enteral nutrition and parenteral nutrition for elderly patients?
Enteral nutrition delivers nutrients through the digestive system, which is the preferred route when possible, as it allows for natural nutrient absorption. Parenteral nutrition, on the other hand, delivers nutrients intravenously, typically used when the digestive system cannot absorb nutrients adequately.
In summary, PEG tubes are valuable tools for delivering enteral nutrition to elderly patients who have difficulty eating or swallowing. They come with several advantages, such as providing essential nutrients, reducing aspiration risk, and simplifying medication administration. However, they are not without drawbacks, including the invasive nature of the procedure, potential loss of oral enjoyment, and ethical considerations. The choice between enteral and parenteral nutrition depends on the individual patient's condition and needs, and a nutrition support team plays a vital role in assessing and managing these options. Additionally, technology, such as feeding pump calculator apps and remote proctored exams, aids healthcare professionals in providing the best care possible to elderly patients requiring enteral nutrition.
What are the considerations for administering Nepro 1.8 tube feeding, and how does it relate to the confirmation of NG tube placement and the choice between continuous vs. intermittent suction NG tube?
When administering Nepro 1.8 through tube feeding, it is crucial to first confirm NG (nasogastric) tube placement to ensure that the enteral tube is correctly positioned in the stomach to deliver nutrition effectively and safely. The feeding tube placement is typically confirmed by a pH test of the aspirate or an x-ray. Once placement is verified, the healthcare provider can decide on the feeding regimen using an enteral feeding pump. The choice between continuous and intermittent suction NG tube methods will depend on the patient's needs and tolerance. Continuous feeding is a steady infusion of formula over 24 hours, which can be beneficial for patients who need a slow, consistent supply of nutrition. Intermittent suction involves delivering the formula at specified intervals, allowing rest periods in between, which may be preferred for patients transitioning to oral feeding or those with better digestive function. Administering Nepro 1.8 or any tube feeding requires careful monitoring for tolerance and signs of complications.
What is a nasogastric (NG) feeding tube, and how is it inserted?
A nasogastric (NG) feeding tube is a flexible plastic tube that is inserted through the nose, down the esophagus, and into the stomach. It's used for feeding when oral intake is not adequate. The insertion process requires skill to ensure the tube is correctly placed in the stomach, usually confirmed by an X-ray.
Are there anti-reflux valves for NG tubes?
Yes, some NG tubes are equipped with anti-reflux valves. These valves are designed to prevent gastric contents from flowing back into the esophagus, reducing the risk of aspiration and pneumonia. This feature is particularly beneficial for elderly patients who might be at higher risk of reflux complications.
How do feeding pumps and dose calculators improve the feeding process?
Feeding pumps and rate/dose calculators help in delivering nutrition at a consistent and controlled pace. This is crucial for elderly patients who may not tolerate large volumes of feed at once. By adjusting the pump rate or using a dose calculator, caregivers can ensure that the patient receives the right amount of nutrition over a suitable period, minimizing complications like aspiration or diarrhea.
Can feeding tubes be used for animals, such as cats?
Yes, feeding tubes are not limited to human use; they are also used in veterinary medicine. For instance, a feline feeding tube might be recommended for cats that cannot eat orally due to illness or surgery. These tubes can be nasogastric or placed directly into the stomach (gastrostomy) depending on the animal's needs and condition.
What is a hepatic enteral formula, and why is Abbott mentioned in this context?
Hepatic enteral formulas are specially designed nutritional feeds for patients with liver disease, providing a balance of nutrients that support liver function while minimizing liver stress. Abbott is a healthcare company that produces various medical foods, including hepatic enteral formulas. These products are formulated to meet the specific dietary needs of patients with liver conditions.
What is Isosource tube feeding?
Isosource is a brand of enteral nutrition formulas intended for tube feeding. It offers a range of products designed to meet the nutritional needs of patients with different medical conditions, including those who require long-term feeding support. Isosource formulas can be used with NG tubes, gastrostomy tubes, and other types of feeding tubes.
Pros of Feeding Tubes in the Elderly:
- Nutritional Support: They provide a direct way to ensure the elderly receive adequate nutrition, especially when oral intake is compromised.
- Medication Administration: Medications can be delivered easily and effectively through the tube.
- Flexibility: Different types of tubes and formulas can be used depending on the patient's condition and nutritional needs.
Cons of Feeding Tubes in the Elderly:
- Infection Risk: There's a risk of infection at the insertion site or within the gastrointestinal tract.
- Discomfort and Complications: Insertion and presence of the tube can cause discomfort, nasal irritation, or more serious complications like aspiration pneumonia.
- Psychological Impact: The presence of a feeding tube can affect the patient's quality of life and may have psychological impacts due to changes in the way nutrition is received.
What are the considerations for the use of feeding tubes in the elderly?
The decision to use a feeding tube in an elderly patient must consider the individual's overall health, prognosis, and personal wishes. The goal is to improve or maintain the patient's nutritional status without compromising their comfort or quality of life. It's important to have a thorough discussion with healthcare providers and family members to make an informed decision that aligns with the patient's values and healthcare goals.
What is enteral tube feeding, and how does it relate to the elderly?
Enteral tube feeding is a method to provide nutrition directly into the stomach or small intestine through a tube. It's often considered for elderly patients who cannot meet their nutritional needs due to difficulty swallowing, decreased appetite, or certain medical conditions. This method ensures they receive the necessary nutrients, fluids, and medications.
Can you explain the difference between an NG tube and a G-tube?
An NG (Nasogastric) tube is a temporary solution, inserted through the nose down to the stomach, ideal for short-term feeding. Taping the NG tube properly is crucial to secure it and prevent displacement. A G-tube (Gastrostomy tube), on the other hand, is placed directly into the stomach through the abdominal wall, suitable for long-term use. A G-tube belt can be used, especially for babies, to secure the tube and minimize the risk of pulling or dislodgement.
What is Dobhoff tube placement, and is there a video guide available?
Dobhoff tube placement involves inserting a special type of feeding tube, designed for more prolonged use in the small intestine, usually for patients who cannot tolerate stomach feeding. Video guides, like a Dobhoff placement video, can provide visual aid and detailed instructions for healthcare professionals and caregivers, illustrating the correct and safe procedure for insertion.
What is the purpose of venting a PEG tube, and how is it done?
Venting a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube is a process used to release gas from the stomach, relieving discomfort and bloating in patients. This procedure involves opening the external portion of the PEG tube to allow gas to escape, which can be a crucial part of patient care.
Where can I find G-tube training certification near me?
G-tube training certification programs are offered by various healthcare institutions and organizations. These programs are designed to educate caregivers and healthcare professionals on the proper care, maintenance, and use of gastrostomy tubes, including practical skills and knowledge on enteral nutrition therapy. Searching for local hospitals, nursing schools, or online platforms can help locate a certification program near you.
What are the pros and cons of enteral nutrition therapy in the elderly?
Pros:
- Ensures adequate nutritional intake when oral intake is not sufficient.
- Can be tailored to meet individual nutritional and caloric needs.
- Reduces the risk of aspiration in patients with swallowing difficulties.
Cons:
- Risk of tube displacement or complications, such as infections at the insertion site.
- Potential for gastrointestinal issues, including diarrhea and bloating.
- Psychological and social impacts, as it can affect the patient's quality of life and independence.
What types of enteral tubes are available, and how are they chosen for the elderly?
Several types of enteral tubes are available, including NG tubes for short-term use, G-tubes for long-term stomach feeding, and PEG tubes for direct insertion into the stomach through the abdominal wall. The choice of tube depends on the patient's condition, nutritional requirements, expected duration of tube feeding, and potential for recovery of normal feeding. The decision involves careful consideration by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers, including physicians, nutritionists, and speech therapists.
What are the benefits of using nasal tubes (NGT feeding) for elderly patients?
A: Nasal tubes, or nasogastric (NGT) feeding tubes, offer a non-surgical option for short-term nutritional support in elderly patients who have difficulty swallowing or cannot consume enough nutrients by mouth. They can be quickly inserted, providing an immediate solution for nutritional deficiencies and improving overall health and well-being.
Are there any alternatives to Jevity 1.5 that can be used with feeding tubes?
Yes, there are several substitutes for Jevity 1.5 that can be used in feeding tubes, including other commercially prepared enteral nutrition formulas designed to meet the specific dietary needs of patients. It's important to consult with a dietitian to choose the most appropriate formula based on the individual's health status, nutritional requirements, and any specific medical conditions.
How do feeding syringes compare to feeding tubes in elderly care? Feeding syringes are typically used for hand feeding or administering medications through feeding tubes and are not a substitute for feeding tubes themselves. They can be used for bolus feeding, where a specific amount of nutritional formula is given directly into the tube at set times, offering a level of manual control over the feeding process.
What are the concerns associated with force feeding through feeding tubes in the elderly?
Force feeding, or the aggressive administration of nutrition without the patient's consent, raises ethical and medical concerns, particularly in elderly patients with advanced dementia or those who are terminally ill. It can lead to discomfort, aspiration pneumonia, or other complications. Decisions about feeding tube use should involve careful consideration of the patient's quality of life, overall health goals, and, when possible, the patient's or their family's wishes.
What feeding tube options are available for elderly patients, and how do they differ?
Feeding tube options for elderly patients include nasogastric (NGT) tubes, which are inserted through the nose into the stomach for short-term use, and more permanent solutions like percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes, which are inserted through the abdomen directly into the stomach. The choice between these options depends on the patient's condition, the expected duration of tube feeding, and the overall care goals.
Can nasal tubes be a long-term solution for elderly patients requiring tube feeding?
While nasal tubes (NGT) are commonly used for short-term nutritional support, they are generally not recommended for long-term use due to the risk of nasal irritation, discomfort, and the potential for displacement. For patients requiring long-term tube feeding, alternative methods such as PEG tubes may be considered more appropriate.
Pros:
- Immediate nutritional support for patients unable to eat orally
- Non-surgical option for short-term use
- Can be used to administer medications and hydration
Cons:
- Risk of nasal and throat discomfort
- Not suitable for long-term use
- Potential ethical concerns with force feeding
It's crucial to consider the individual needs of the elderly patient and to discuss the potential benefits and drawbacks of feeding tube use with healthcare professionals to ensure the best possible care approach.
Our Resources section can help you find the information and tools that you need. We have courses, videos, checklists, guidebooks, cheat sheets, how-to guides and more.
You can get started by clicking on the link below. We know that taking care of a loved one is hard work, but with our help you can get the support that you need.
Click here to go to Resources Section now!





