Fall Prevention for the Elderly: Essential Strategies to Avoid Serious Injury
Discover essential strategies for preventing falls among the elderly, including managing health risks, environmental safety tips, and the benefits of using Indeelift for safe recovery. Learn how to protect older adults from serious injuries and enhance their independence.
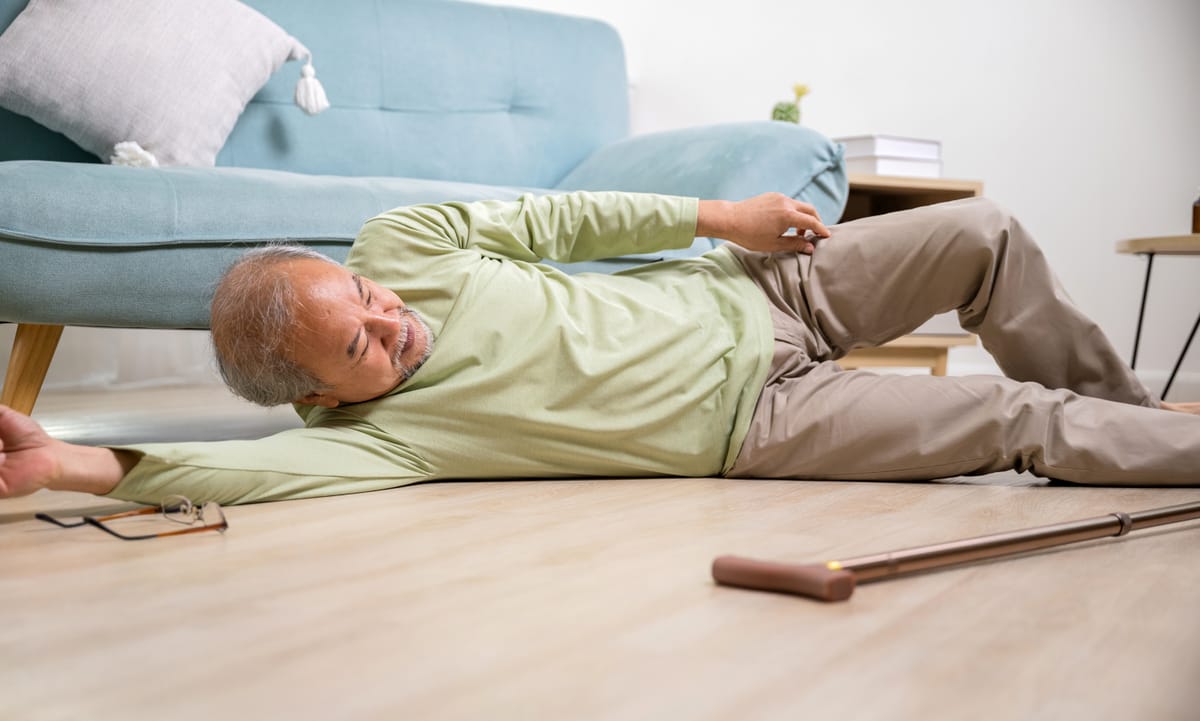

Fall: The elderly may have risk factors that may cause serious injuries
The Gravity of Falls among the Elderly
Falls are not just accidents but significant risks for older adults, leading to serious injuries, diminished independence, and high medical costs. Understanding the gravity of fall-related issues is crucial for preventing them and ensuring the safety of our elderly population.
The Alarming Statistics of Falls in the Elderly
This section will delve into the prevalence of falls among the elderly, highlighting the high incidence of serious injuries like hip fractures, head trauma, and the subsequent medical costs and emergency department visits. It will underscore the public health perspective, noting falls as the leading cause of injury and loss of independence among older persons
Listen to the podcast on a fall recovery tool that is helping seniors remain in their homes.
Fall:Elderly and Injurious Falls
Falls among the elderly constitute a significant public health issue, with a multitude of risk factors contributing to the high incidence of falls and subsequent serious injuries. The fear of falling, prevalent among older adults, is not unfounded, as falls are the leading cause of serious injuries such as hip fractures and head trauma in this age group. These injuries often lead to substantial medical costs, including emergency department visits and prolonged hospital stays. The complexity of fall-related injuries is compounded by the presence of multiple risk factors, including poor health, chronic conditions like high blood pressure, and the effects of both prescription and nonprescription medications, which can increase the likelihood of falls by affecting balance, muscle strength, and cognitive function.
Environmental Hazards
Environmental hazards in the home, such as poor lighting, slippery floors, and loose rugs, further exacerbate the risk, making falls more likely to occur. Additionally, impaired vision and declining muscle strength make navigating these hazards even more challenging for elderly persons, increasing their risk of falling. Recurrent falls, which are common in this demographic, not only result in physical injuries but also lead to a fear of falling again, creating a cycle that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and independence.
Introducing a Fall Prevention Program in the Home
To address these concerns, fall prevention strategies are paramount. These include regular physical examinations to monitor health conditions and medication side effects, as well as physical therapy and exercise programs designed to improve balance, muscle strength, and flexibility.
Tai chi, in particular, has been recognized for its benefits in improving balance and reducing the risk of falls among older adults. Additionally, making environmental modifications to improve home safety, such as installing grab bars in the bathroom, improving lighting, and removing tripping hazards, can significantly reduce the risk of falls.

Request a Home Safety Evaluation
Occupational therapists play a crucial role in assessing the home environment for potential hazards and recommending modifications to ensure safety. They, along with physical therapists, can also provide personalized exercise programs that cater to the specific needs of older adults, helping to build strength and improve balance. Furthermore, the adoption of walking aids for those with declining function can provide additional support and stability, reducing the risk of falls.
Importance of Vitamin D Supplements
Public health initiatives and family medicine practitioners emphasize the importance of vitamin D supplementation, especially in older patients with fragile bones, as it has been shown to improve muscle function and bone health, further mitigating the risk of falls and fractures. Regular laboratory tests to monitor health indicators, along with a comprehensive approach to managing chronic illnesses and their symptoms, are also vital components of an effective fall prevention strategy.
Falls in older adults are a multifaceted issue that requires a comprehensive approach for prevention and management.
We can significantly reduce the incidence of falls and the severe injuries they cause.
By addressing the various risk factors from:
Health conditions
Medication side effects
Environmental hazards
Impaired physical function
While implementing targeted prevention strategies. This not only helps to reduce healthcare costs associated with fall-related injuries but also supports the well-being and independence of the elderly population, ensuring they can lead active and fulfilling lives without the constant fear of falling
Understanding Risk Factors for Falls
Health Conditions and Medication: Amplifying Fall Risks in the Elderly
Poor health and chronic conditions such as high blood pressure and cognitive impairment significantly amplify the risk of falls among older adults. These health issues, common in the elderly, can impair balance, reduce muscle strength, and slow reaction times, making falls more likely and more dangerous. High blood pressure, for instance, can lead to dizzy spells or fainting episodes, directly increasing the risk of a fall. Cognitive impairments, including conditions like Alzheimer's disease or dementia, not only affect memory and judgment but also the physical ability to navigate safely, thus elevating the potential for serious injury from falls.
The use of prescription and nonprescription medications adds another layer of risk. Many medications have side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, or even drops in blood pressure upon standing, all of which can precipitate a fall. Polypharmacy, the use of multiple medications, is particularly prevalent among the elderly and further exacerbates these risks. This complex interplay of health conditions and medication management necessitates vigilant monitoring and regular physical examinations to mitigate the increased risk of falls and subsequent serious injuries, including hip fractures and head trauma, which lead to high medical costs and emergency department visits.
Moreover, these health-related fall risks contribute significantly to the fear of falling among older adults. This fear can lead to reduced activity levels, which paradoxically increases the risk of falls by leading to muscle weakness and reduced mobility. Addressing these health and medication-related fall risks through family medicine, regular check-ups, and tailored exercise programs, such as tai chi, can help improve balance and muscle strength, thereby reducing the incidence of falls and the fear associated with them.
Environmental Hazards: The Silent Contributors to Falls
Environmental factors in the home setting, such as poor lighting, slippery floors, and clutter, significantly contribute to the risk of falls among the elderly. Poor lighting can obscure obstacles and hazards, making it difficult for older adults, especially those with impaired vision, to navigate safely. Slippery floors, whether from spills, polished surfaces, or unsuitable footwear, are common culprits behind falls, often leading to serious injuries such as broken bones and head injuries. Other environmental hazards, including loose rugs, electrical cords across walkways, and unstable furniture, further increase the risk of falls, making environmental safety a critical aspect of falls prevention.
Addressing these environmental hazards is a crucial step in preventing falls and ensuring the safety of elderly persons within their homes. Simple modifications, such as improving lighting, securing rugs, and organizing cords and clutter, can significantly reduce fall risks. Moreover, the role of occupational therapists in assessing homes for fall risks and recommending safety modifications is invaluable. They, along with physical therapists, can also suggest the use of walking aids for those with declining function, providing additional support and stability.
Preventive measures also include public health initiatives aimed at raising awareness of fall risks and how to mitigate them through environmental safety measures. These efforts, combined with personal and community action, can substantially reduce the incidence of falls, helping older adults maintain their independence and quality of life while minimizing the fear of falling. Through a comprehensive approach that addresses both health conditions and environmental hazards, the risk of falls among the elderly can be significantly reduced, leading to fewer injuries, reduced medical costs, and a better overall quality of life for older adults.
Strategies for Fall Prevention
The Role of Physical Therapy and Exercise
How engaging in physical therapy and exercises like tai chi can improve balance, muscle strength, and reduce the risk of future falls. The importance of physical therapists in guiding older adults through exercises tailored to their needs will be emphasized.

Medication Management and Health Monitoring: Key Pillars in Fall Prevention
Effective medication management is essential in reducing the risk of falls among the elderly. Many older adults take multiple medications, both prescription and nonprescription, which can have side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, or even blood pressure fluctuations, all of which significantly increase the risk of falling. Healthcare providers, particularly those in family medicine and geriatrics, play a critical role in reviewing and adjusting medications to minimize these side effects.
Regularly scheduled physical examinations allow for the monitoring of health conditions that may affect balance and mobility, such as cognitive impairment, muscle weakness, and sensory deficits. By closely managing and adjusting treatments as necessary, healthcare providers can help older adults maintain better control over their health, reducing the incidence of falls and the serious injuries they can cause, such as broken bones, hip fractures, and head trauma.
Furthermore, the implementation of vitamin D supplements is increasingly recognized for its role in fall prevention. Adequate levels of vitamin D contribute to improved muscle function and bone health, reducing the risk of falls and the severity of fall-related injuries. Regular laboratory tests to monitor vitamin D levels and other health indicators are an important aspect of health monitoring for the elderly, ensuring that any deficiencies are identified and addressed promptly.
Home Safety Modifications: Creating a Fall-Proof Living Environment
Making practical modifications to the home environment is crucial in preventing falls among elderly persons. Occupational therapists and physical therapists can provide valuable insights into the specific needs of an individual, recommending changes that can make a significant difference in safety. Installing grab bars in critical areas such as the bathroom, beside the toilet, and in the shower can provide essential support for older adults. Improving lighting throughout the home, especially in stairways, hallways, and night paths to the bathroom, can help prevent falls by ensuring that obstacles and hazards are clearly visible.
Reducing clutter is another important step in creating a safer living environment. By keeping floors clear of unnecessary items, cords, and rugs that can trip, the risk of falls is significantly decreased. Furthermore, ensuring that commonly used items are easily accessible without the need for reaching up high or bending down low can prevent risky movements that might lead to a fall.
Environmental safety also involves evaluating the need for walking aids or adaptive devices to assist with mobility. For those with declining function, a walking aid can provide the additional stability needed to navigate the home safely. Physical therapy exercises focused on strengthening and balance can further enhance mobility and reduce the risk of falls.
In summary, managing medications to minimize side effects, conducting regular health monitoring through physical examinations and laboratory tests, and making targeted home safety modifications are all pivotal strategies in preventing falls among the elderly. These measures not only safeguard against the immediate risk of falls but also contribute to a broader public health goal of reducing the incidence of serious injuries, hospital visits, and the overall impact of falls on the health and independence of older adults. Through a comprehensive approach that combines medication management, health monitoring, and environmental safety, the risk of falls and their devastating consequences can be significantly mitigated, enabling older persons to lead safer, more active lives.
Innovative Solutions for Fall Recovery
Highlighting the importance of having a plan for fall recovery, including the introduction of tools like the Indeelift - termed the "people picker-upper" - that help seniors get up safely after a fall. The role of such devices in ensuring elderly individuals can participate in activities like gardening, exercising, and playing with grandchildren without fear will be explored.
The Psychological Impact of Falling: Navigating the Fear Among Older Adults
An examination of how the fear of falling affects older adults, leading to decreased activity levels, social isolation, and a decline in physical health. The importance of addressing this fear through education, support, and the use of safety devices will be discussed.
The fear of falling represents a profound psychological impact on older adults, significantly influencing their behavior, lifestyle, and overall well-being. This fear, often rooted in the experience of a previous fall or the awareness of being at high risk for falls, can lead to a cycle of decreased activity levels, social isolation, and a subsequent decline in physical health. The dread of experiencing serious injuries, such as broken bones, hip fractures, or head trauma, exacerbates this fear, making it a pivotal concern in elderly care and falls prevention strategies.
Decreased activity levels are one of the most direct consequences of the fear of falling.
Older adults, anxious about the risk of injury, may reduce their engagement in physical exercise and daily activities. This reduction not only limits their social interactions and opportunities for maintaining physical strength and balance, such as through tai chi or other exercise programs but also contributes to a decline in muscle strength and flexibility. As a result, the paradoxical effect is an increased risk of falls and subsequent serious injuries, further fueling the cycle of fear.
Social isolation is another significant effect of the fear of falling. Older adults may avoid leaving their homes, participating in social activities, or even engaging with family and friends due to the anxiety associated with falling in public or being unable to navigate environmental hazards safely. This isolation can lead to feelings of loneliness, depression, and a decline in mental health, compounding the challenges associated with aging and poor health.
The decline in physical health, driven by reduced activity and social engagement, can exacerbate existing health conditions, such as high blood pressure, cognitive impairment, and fragile bones, increasing the necessity for medical interventions, prescription and nonprescription medications, and possibly leading to more frequent visits to emergency departments. The interconnectedness of physical and psychological health underscores the importance of addressing the fear of falling holistically.
Addressing the Fear of Falling
Addressing the fear of falling requires a multifaceted approach that includes education, support, and the strategic use of safety devices and modifications. Educating older adults and their families about the risk factors for falls, preventive measures, and ways to safely increase activity levels can empower them to take proactive steps towards fall prevention. Support from healthcare providers, including family medicine practitioners, physical therapists, and occupational therapists, is crucial in developing personalized fall prevention and physical therapy programs that account for individual health conditions and risks.
The use of safety devices, such as walking aids, and home modifications, like improving lighting, installing grab bars, and reducing environmental hazards, can provide older adults with the confidence to maintain their mobility and independence safely. Additionally, public health initiatives that promote environmental safety, regular physical examinations, and the importance of vitamin D supplements for maintaining bone health are vital components of a comprehensive strategy to reduce falls and alleviate the fear associated with them.
In conclusion, the psychological impact of falling among older adults is a critical aspect of falls prevention and elderly care. By addressing the fear of falling through education, support, and practical measures to improve safety and health, it is possible to enhance the quality of life for older adults, encouraging them to remain active, socially connected, and confident in their ability to navigate their environment safely.
The Economic Burden of Falls: Assessing the Impact on the Elderly and Healthcare System
Fall are the #1 Independence Robber of Seniors
Falls among the elderly not only pose significant health risks but also bring about substantial economic burdens, affecting individuals, families, and the broader healthcare system. The direct costs, including emergency department visits, hospitalizations, surgeries for injuries such as hip fractures and head trauma, and long-term care requirements, are just the tip of the iceberg. Indirect costs, such as lost productivity, the need for family members to take time off work to care for the injured individual, and the long-term impact on the quality of life and independence of older adults, further compound the economic strain.
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations represent a significant portion of the medical costs associated with falls. With older adults at high risk of serious injuries from falls, such as broken bones and head injuries, the need for acute medical care and possibly surgical intervention is high. Hip fractures, one of the most common and serious fall-related injuries, often require surgery followed by extended hospital stays and rehabilitation, leading to considerable healthcare expenses. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that falls are the leading cause of injury-related emergency department visits among older adults, underscoring the prevalence and financial impact of this issue.
Long-term care needs, whether in a nursing home setting or through home health services, add another layer to the economic burden. For those who experience a decline in physical function or cognitive impairment as a result of a fall, the need for ongoing care can result in significant costs, both for out-of-pocket expenses and for the healthcare system at large. The use of prescription and nonprescription medications to manage pain, prevent future falls, or treat the underlying conditions contributing to falls further adds to the financial strain on individuals and families.
The Indirect Costs of Falls
The indirect costs associated with falls are equally daunting. The loss of independence and the subsequent need for family members to provide care or adjust their work schedules can lead to lost wages and productivity, not to mention the emotional and physical toll on caregivers. Additionally, the fear of falling again can lead to decreased mobility and social isolation for the elderly, potentially resulting in further health decline and associated costs.
Preventive measures, such as regular physical examinations to assess fall risk, physical therapy to improve balance and muscle strength, and environmental modifications to reduce hazards, are crucial in mitigating the risk of falls and, by extension, reducing their economic impact. Public health initiatives aimed at fall prevention, including education on the safe use of prescription and nonprescription medications, the importance of vitamin D for bone health, and the benefits of exercise programs like tai chi for maintaining strength and balance, are vital components of a comprehensive approach to reducing falls among the elderly.
In conclusion, the economic burden of falls on the elderly and the healthcare system is multifaceted, encompassing direct medical costs and a wide range of indirect costs. By understanding these impacts and investing in preventive strategies, it is possible to not only improve the health and well-being of older adults but also alleviate the financial strain on individuals, families, and healthcare providers. Through a concerted effort involving healthcare professionals, public health initiatives, and family support, the cycle of falls and their economic consequences can be broken, ensuring a safer, more secure future for the elderly population
The Role of Family and Caregivers in Fall Prevention and Fall Recovery Plan
Guidance for families and caregivers on how they can support their elderly loved ones in preventing falls, including tips for encouraging exercise, ensuring medication safety, and making homes safer.
Implementing a comprehensive fall recovery plan is a critical step in ensuring the safety and well-being of older adults, particularly those at high risk of falling due to various factors such as poor health, chronic conditions like high blood pressure and cognitive impairment, and the use of medications that may affect balance and coordination. One innovative solution that addresses the immediate aftermath of a fall is the introduction of the Indeelift, a device designed to safely assist seniors in getting up from the floor without the need for manual lifting, thus significantly decreasing the stress and strain on the caregiver's body.
The Indeelift, often referred to as a human floor lift, is engineered to empower seniors, offering them a way to independently and safely rise to a standing or seated position after a fall. This tool is invaluable in mitigating the risks associated with falls, such as serious injuries including broken bones, hip fractures, and head trauma. By providing a means for effortless recovery, the Indeelift not only enhances the autonomy of older adults but also significantly reduces the potential for further injury during the lifting process, a common concern for both the fallen individual and their caregivers.
For caregivers, whether family members or healthcare professionals, the physical demand and risk of injury from lifting or assisting a fallen senior can be considerable. The Indeelift addresses this concern head-on, offering a practical solution that protects caregivers from back strain, muscle pulls, and other injuries that can occur when manually lifting someone. This reduction in physical strain is crucial, as it ensures that caregivers remain healthy and capable of providing ongoing support and care.
The Benefits of Indeelift, the People Picker Upper
The benefits of having an Indeelift in the home or care setting are manifold. For seniors, the device promotes a sense of security, knowing that in the event of a fall, they have a reliable means of getting up safely, thus reducing the fear of falling that many older adults experience. This fear can lead to decreased activity levels, social isolation, and further physical decline, exacerbating the risk factors for falls. By alleviating this fear, the Indeelift encourages more active and engaged lifestyles among seniors, contributing to better overall health and reducing the likelihood of future falls.
In every home graced by the wisdom and memories of seniors, the presence of Indeelift stands as a testament to their continued independence and dignity. This revolutionary tool is not just an appliance; it's a beacon of self-reliance, designed specifically to uphold the autonomy of our elders right within the comfort of their own homes.
The genesis of Indeelift was born from a place of love and necessity. Its creator, who found himself in the role of caregiver for his beloved parents, encountered a harsh reality when they began to experience falls—a common and distressing challenge for many seniors. The revelation that the safest method to assist a senior off the floor was to summon local EMS providers struck him as both shocking and impractical. It highlighted a significant gap in care and support within the very sanctuaries of our elders' homes.
Motivated by this experience, he envisioned a solution that would not only safeguard the well-being of his parents but also empower seniors everywhere to maintain their independence. Indeelift was created to be that solution. It is ingeniously designed to safely lift individuals from the floor to a seated or standing position, minimizing the risk of injury for both the senior and their caregivers.
Indeelift's impact extends far beyond its immediate functionality. It embodies a movement towards creating environments where seniors can navigate their daily lives with confidence, knowing that help is at hand should they ever find themselves in need. Its presence in every senior's home symbolizes a commitment to their safety, autonomy, and respect—core values that guide families in caring for their aging loved ones.
As Indeelift becomes a staple in homes across the nation, it not only aids in preventing the physical strain associated with falls but also alleviates the psychological stress tied to dependency. Seniors can flourish in their later years with grace, surrounded by the familiar comforts of home, and families can rest easier, knowing their loved ones have the support they need to live safely and independently.
The story of Indeelift is more than just a tale of innovation; it's a reflection of our society's dedication to honoring and empowering our seniors. By integrating this tool into every senior's home, we are collectively taking a significant step towards a future where every elder can enjoy their golden years with the dignity, respect, and independence they so richly deserve
Furthermore, from a public health perspective, the widespread implementation of Indeelift devices can contribute to a decrease in emergency department visits and medical costs associated with fall-related injuries. By enabling prompt and safe recovery from falls, the Indeelift can help prevent the complications that often arise from prolonged immobility on the floor, such as pressure sores, muscle weakness, and increased susceptibility to subsequent falls.
In conclusion, the Indeelift represents a significant advancement in fall recovery and prevention strategies for older adults. By addressing the immediate needs following a fall and providing a safe, stress-free lifting solution, the Indeelift not only safeguards the health and independence of seniors but also protects caregivers from the physical and emotional toll of fall-related incidents. Promoting the adoption of an Indeelift for every senior at risk of falling is a proactive step toward enhancing the quality of life for older adults and ensuring a safer, more supportive environment for all involved.
Community and Healthcare Initiatives
An overview of public health initiatives, community programs, and healthcare policies aimed at reducing falls and supporting the health and independence of the elderly population. The role of occupational therapists, family medicine, and public health efforts in fall prevention will be highlighted.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for Fall Prevention
A concluding section that emphasizes the collective responsibility of individuals, families, healthcare providers, and communities in preventing falls among the elderly. It will call for increased awareness, education, and action to safeguard the well-being and independence of older adults.
FAQ: Fall Prevention and Recovery for Older Adults
What are the main risk factors for falls among older adults?
The primary risk factors include poor health, impaired vision, muscle weakness, environmental hazards, and the side effects of prescription and nonprescription medications. Conditions like cognitive impairment and acute illnesses also significantly increase the risk.
How can tai chi help in preventing falls in older persons?
Tai chi is a gentle exercise that improves balance, muscle strength, and flexibility, reducing the risk of falls by enhancing physical stability and coordination.
Why are hip fractures a significant concern for the elderly following a fall?
Hip fractures are serious injuries that can result from falls, leading to prolonged hospital stays, surgery, and rehabilitation. They represent a leading cause of decreased mobility and independence among older adults.
What role do physical therapists play in falls prevention?
Physical therapists design personalized exercise programs to improve balance, strength, and mobility, significantly reducing the risk of falls and subsequent injuries.
How does poor lighting contribute to falls, and what can be done to improve safety?
Poor lighting can obscure hazards and obstacles, increasing the risk of trips and falls. Improving lighting, especially in hallways, staircases, and bathrooms, can greatly enhance environmental safety for older adults.
Can vitamin D supplements reduce the risk of falls in older adults?
Yes, vitamin D supplements can improve muscle function and bone health, reducing the risk of falls and fractures by strengthening the physical framework of the body.
How do emergency departments play a role in the care of older patients who have fallen? Emergency departments provide immediate care for injuries resulting from falls, such as head injuries and broken bones. They also initiate assessments for underlying risk factors that may contribute to future falls.
What is the importance of a physical examination in preventing falls among the elderly? Regular physical examinations help identify health conditions that increase the risk of falls, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments to medications and treatments to mitigate these risks.
How do environmental hazards in the home increase the risk of falls for elderly persons? Environmental hazards such as slippery floors, loose rugs, and clutter can easily lead to trips and falls. Addressing these hazards through home safety modifications is crucial in preventing falls.
What strategies can be employed to prevent future falls in older adults?
Preventive strategies include engaging in regular physical activity, ensuring proper nutrition, making environmental modifications for safety, managing medications to minimize side effects, and using assistive devices like walking aids when necessary.



