Depression Et Hallucination: Can Depression Cause Hallucinations?
"Depression Et Hallucination: Can Depression Cause Hallucinations?" explores the lesser-known connection between severe depression and hallucinations. This episode delves into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, helping listeners understand the impact of depression on reality perception.

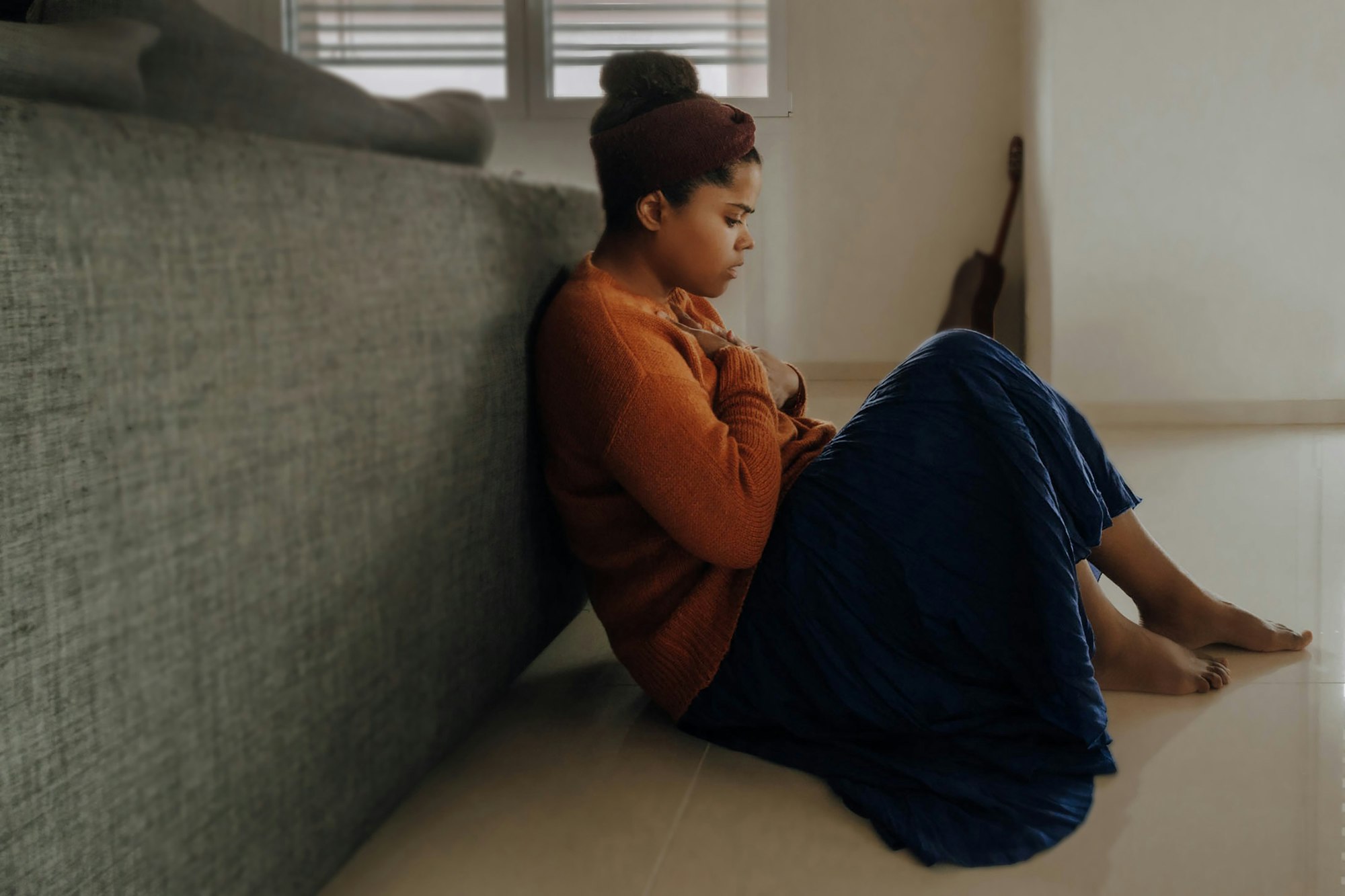
Depression and hallucinations are two mental health issues that can have a major impact on a person’s life. While depression is a common mental health disorder, hallucinations are much less common, but can still be very disruptive when they occur. This article will discuss the link between depression and hallucinations, outline possible causes of depression-induced hallucinations, and provide advice on how to cope when they occur.
Many people don’t realize just how closely linked depression and hallucinations are, and this article will help shed light on the subject. Depression, particularly major depression, is a major mental health disorder that affects millions of people, and can be caused by various environmental and biological factors. Hallucinations, meanwhile, are an alteration in perception where a person can see, smell, hear, or feel something that isn’t actually there. While hallucinations are rare, they can be extremely distressing when they do occur.
For some people, depression can lead to hallucinations, though the exact mechanism behind this connection is not fully understood yet. It is thought that the combination of low mood, anxiety, and stress associated with depression may trigger changes in brain chemistry that can lead to hallucinations. It is also possible that certain medications used to treat depression can cause hallucinations as a side effect. In this article, we will explore the potential connection between depression and hallucinations, and discuss ways to cope when it occurs.
What is Major Depressive Disorder?
Depression is a serious and complex mental illness that affects millions of people around the world. It can have a range of symptoms, from feeling constantly sad to losing interest in activities you once enjoyed. It can also manifest as physical symptoms, such as changes in appetite or sleeping patterns. Symptoms of depression can vary from mild to severe, and can last for a few weeks or longer.
Understanding Psychotic Symptoms in Depression
Psychotic symptoms in depression represent a complex intersection of mental health conditions, where the profound sadness and hopelessness of depression intertwine with the disorienting experiences of psychosis. Psychosis is a break from reality, often characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking and behavior. When these symptoms occur alongside depression, they can be particularly severe and debilitating, significantly impacting a person’s ability to function in daily life.
According to the American Psychiatric Association, psychotic symptoms are a notable feature of major depressive disorder, especially in individuals experiencing severe depression. These symptoms can manifest as auditory and visual hallucinations, where a person might hear voices or see things that aren’t there, as well as delusions, which are strong beliefs in things that are not based in reality. Studies indicate that up to 20% of people with major depressive disorder experience psychotic symptoms, underscoring the importance of recognizing and addressing this condition within the broader context of mental health.
What are Hallucinations?
Hallucinations are sensory experiences that are not real. They can involve any of the five senses; sight, sound, taste, smell and touch. Depending on the type of hallucination, they may be caused by a medical condition, medication, or a substance. Common examples of hallucinations include seeing things that are not there, hearing voices, or experiencing smells that nobody else can detect.
Types of Auditory and Visual Hallucinations
There are several types of hallucinations, including:
- Auditory hallucinations: Hearing something when there is no physical sound present.
- Visual hallucinations: Seeing something that is not actually there.
- Olfactory hallucinations: Smelling something that isn't really there.
- Tactile hallucinations: Feeling something that is not actually touching you.
- Gustatory hallucinations: Tasting something that isn't really there.
What is Psychotic Depression?
Psychotic depression, also known as major depressive disorder with psychotic features, is a severe mental health condition that combines the intense emotional lows of depression with the disorienting effects of psychosis. This type of depression is marked by a blend of depressive symptoms—such as persistent sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities—and psychotic symptoms, including hallucinations and delusions.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5), classifies psychotic depression as a subtype of major depressive disorder. According to the DSM-5, psychotic depression is defined by the presence of a major depressive episode accompanied by psychotic symptoms. These hallucinations and delusions can make it challenging for individuals to distinguish between what is real and what is not, further complicating their mental health struggles. Understanding and identifying psychotic depression is crucial for providing appropriate treatment and support to those affected.
The Link Between Depression and Hallucinations
Depression is a mental health condition that can be long lasting and severely disabling for those who experience it. It’s a complicated condition with many possible causes, but one thing is certain - depression can lead to a host of other issues, including hallucinations.
Depression can sometimes lead to the development of a psychotic disorder, where individuals experience hallucinations and delusions.
Hallucinations are defined as sensory experiences that occur without external stimuli. They can involve any of the five senses - sight, sound, taste, touch and smell. Depression-induced hallucinations are particularly interesting because they can often be attributed to psychological causes, such as feelings of guilt or fear.
In recent years, research has been conducted to better understand the link between depression and hallucinations. While the studies have yet to conclusively prove a definite relationship, there is evidence to suggest that depression is a risk factor for developing delusional thoughts and sensory disturbances.
Various studies have found that people with depression are more likely to experience hallucinations than those without the disorder. One study, conducted in 2017, found that 53% of participants with major depressive disorder reported having experienced at least one hallucination. Another study, in 2018, found that 61% of participants with major depressive disorder and psychotic features experienced auditory hallucinations.
These studies demonstrate a clear link between depression and hallucinations, which suggests that depression may be one of the factors involved in causing these experiences. Further research is needed to explore this connection in more detail, but the results of these studies give us an insight into the potential causes of depression-induced hallucinations.
Causes of Depression-Induced Psychotic Symptoms
Hallucinations connected to depression can be caused by a combination of psychological and biological factors. These can range from trauma and stress, to the effects of certain medications and changes in the brain chemistry.
Hallucinations can also be a symptom of various psychotic disorders, which include conditions like schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
Psychological factors can play a role in triggering depression related hallucinations. Trauma and chronic stress can both lead to a decrease in serotonin levels, which can lead to mental health issues such as depression. It’s known that people who have experienced trauma may be at greater risk of developing depression-induced hallucinations.
Biological factors can also affect the development of these hallucinations. Certain medications can have side-effects that affect the mind, leading to a heightened sense of fear and paranoia. This can in turn lead to hallucinations, as the mind tries to make sense of the confusing information it is receiving.
Changes in the chemistry of the brain, including serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine, can all contribute to depression and its symptoms. Low levels of these chemicals can trigger abnormal activity in the brain, resulting in hallucinations or other symptoms of depression.
It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences depression will experience hallucinations. However, if someone does, it’s important to seek professional help in order to help them manage their symptoms and find a way to deal with any underlying causes.
Risk Factors for Psychotic Depression
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing psychotic depression. These include:
- Family History of Mental Health Conditions: A family history of depression or psychosis can predispose individuals to psychotic depression.
- Trauma or Stress: Experiences of physical or emotional abuse, significant life changes, or chronic stress can trigger psychotic depression.
- Substance Abuse: The use of alcohol or drugs can exacerbate symptoms and increase the risk of developing psychotic depression.
- Sleep Disorders: Conditions like insomnia or sleep apnea can contribute to the onset of psychotic symptoms in depression.
- Other Medical Conditions: Chronic illnesses or persistent pain can also be contributing factors.
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetic factors play a role in the susceptibility to mental health conditions, including psychotic depression.
According to the National Institute of Mental Health, individuals with psychotic depression are at a higher risk of developing other mental health conditions, such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia spectrum disorders. They are also more likely to experience suicidal thoughts and behaviors, making it essential to seek help from a mental health professional. With proper treatment, including medication and therapy, it is possible to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected by psychotic depression.
Examples of Depression-Induced Hallucinations
When depression is severe enough, it can cause what we call “hallucinations.” A hallucination is when you perceive something that isn't actually there. It can come in many forms – from hearing voices to seeing things to feeling like you're being touched or watched.
It's important to remember that hallucinations are very real phenomena for those experiencing them, and that they can be extremely overwhelming and distressing. It's equally important to understand that hallucinations can be a sign of a much larger mental health crisis – one that needs to be addressed by a healthcare professional.
Here are a few examples of how depression can lead to hallucinations:
- Hearing voices or sounds that aren't there.
- Seeing images or objects that aren't real.
- Feeling like someone is watching or following you.
- Feeling like your body is being touched or manipulated.
- Being unable to tell the difference between reality and what you're imagining.
These types of symptoms can be extremely disorienting and can lead to confusion and fear. It's important to note that hallucinations can occur even when you're not depressed – but they can often be more intense and persistent when combined with depression. It's also important to remember that hallucinations can be a sign of other mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
If you're experiencing any type of hallucinations, it's important to seek medical attention and talk to a mental health professional. They can help you talk through your experiences and make sure you get the best possible care for your situation.
Coping With Depression-Induced Hallucinations: When to See a Mental Health Professional
Depression-induced hallucinations can be difficult to cope with. In order to find the best ways to manage the symptoms, it's important to understand that there is usually an underlying cause for them. Here are some tips on how to cope with depression-induced hallucinations:
- Seek Professional Help: It is important to seek help from a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist. This will help to identify the underlying causes of the hallucinations and develop a treatment plan to address them.
- Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help to reduce stress and anxiety levels, which can help to minimize the intensity and frequency of the hallucinations. Examples of these techniques include deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and tai chi.
- Set Realistic Goals: It is important to set realistic goals in order to stay on track with treatment. Making small and achievable goals can help to reduce the stress and anxiety that can lead to depression-induced hallucinations.
- Reach Out and Connect: Connecting with family and friends can be a great way to reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can also contribute to depression-induced hallucinations.
- Engage in Healthy Activities: Activities such as exercise, art therapy, and music therapy can help to reduce stress and improve overall mental health. Participating in these activities can also help to distract from the hallucinations.
- Get Enough Sleep: It is critical to get enough sleep in order to maintain better mental health. Poor sleep hygiene can contribute to symptoms of depression, which can increase the risk of experiencing hallucinations.
By utilizing the above strategies, individuals can learn to better cope with depression-induced hallucinations. However, it is important to remember that everyone is different and what works for one person may not work for another. It is therefore important to seek help from a mental health professional if the symptoms become unmanageable.
Conclusion
Depression and any potential hallucinations associated with it should be taken seriously and monitored closely. It is important to have regular mental health check-ins to ensure these issues are addressed in an appropriate and timely manner. If you are experiencing depression that may be triggering hallucinations, speak to a doctor or mental health professional about the best mode of treatment.
Hallucinations can be a sign of depression, but there are a variety of other causes for them, as well. It is important to know the difference between real events and experiences and those which are false and created by your mind. Exploring any underlying mental health issues can help to prevent and alleviate any potential hallucinations.
Checking in with a mental health professional will allow you to better understand and manage the symptoms of depression and any related hallucinations. With the right support system and treatment plan, it is possible to manage depression and the associated hallucinations. Do not be afraid to reach out for help.
You might also like this article: