Deciphering Corticobasal Degeneration: A Comprehensive Guide on a Rare Dementia Form
Explore the complexities of Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD), a rare neurodegenerative disorder. Learn about its early symptoms, such as movement difficulties and speech issues, challenges in diagnosis, and the overlap with other disorders. Understand CBD's impact on patients and families.

By David Heitz
Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD) is a rare and complex form of dementia, often overshadowed by more common neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. This comprehensive article delves into the intricate aspects of CBD, from its symptoms and progression to the challenges it poses for patients, families, and healthcare providers.
The Radin Family's Journey with CBD The Radin family's experience sheds light on the personal impact of CBD. Gary Radin and his mother, Lisa, faced a daunting journey when Neil Radin, Gary's father, was diagnosed with a frontotemporal-related disorder that was later confirmed as CBD. Neil's early symptoms were subtle, beginning with a lack of focus and initiative, which were initially mistaken for depression. The family's proactive approach, involving a psychological evaluation and brain imaging, led to a diagnosis that explained Neil's declining motor function and speech issues.
Understanding Corticobasal Degeneration and Corticobasal Syndrome
CBD is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by nerve cell loss in specific areas of the brain, including the cerebral cortex and the basal ganglia. This condition leads to corticobasal syndrome (CBS), which manifests as a combination of cognitive, motor, and speech impairments. Unlike Alzheimer's disease or frontotemporal dementia, CBD is marked by distinct movement disorders and muscle rigidity, often affecting one limb (alien limb syndrome).
The mother-son team wrote “What If It’s Not Alzheimer’s?: A Caregiver’s Guide To Dementia with the underline “Features the Latest Information on Frontotemporal Degeneration.”
Early Symptoms and Diagnosis Challenges of Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD)
Corticobasal Degeneration, often abbreviated as CBD, is a rare neurodegenerative disorder that typically manifests between the ages of 50 and 70. The initial symptoms of CBD are subtle yet progressive, beginning with difficulty in controlling movements and muscle spasms in one limb – a phenomenon sometimes referred to as 'alien limb syndrome'. This particular symptom is a distinctive feature of corticobasal syndrome, a condition closely associated with CBD. Patients may notice that one limb seems to act independently or experiences unusual stiffness or movement problems.
Corticobasal degeneration advances
As CBD advances, these motor symptoms often extend beyond a single limb, impacting broader muscle coordination and control. This progression can lead to noticeable changes in how patients perform manual tasks, often requiring interventions such as occupational therapy to maintain independence in daily activities. In addition, the basal ganglia, a group of structures deep within the brain that help regulate movement, are significantly affected in CBD, contributing to these movement disorders.
Alongside motor symptoms, CBD patients frequently encounter difficulties with speech and swallowing. Speech therapy becomes a crucial aspect of their care, addressing problems like slurred speech and the ability to articulate words clearly. Swallowing difficulties can lead to life-threatening complications such as aspiration pneumonia, a severe infection that occurs when food or saliva is inhaled into the lungs.
Cognitive decline in CBD
Cognitive decline is another hallmark of CBD, encompassing memory problems and personality changes. As the disease progresses, the degeneration of brain cells in the cerebral cortex leads to these cognitive impairments. Memory loss, though not as prominent as in Alzheimer's disease, can be a significant challenge, affecting the patient’s ability to recall recent events or familiar tasks.
One of the most challenging aspects of CBD is its diagnosis. The overlap of its symptoms with other neurodegenerative disorders, such as progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and frontotemporal dementia, complicates the clinical diagnosis. While PSP shares similar movement disorders with CBD, its progression and impact on the brain differ. Alzheimer's disease, the most common form of dementia, also shares some cognitive symptoms with CBD but typically lacks the early motor symptoms seen in CBD.
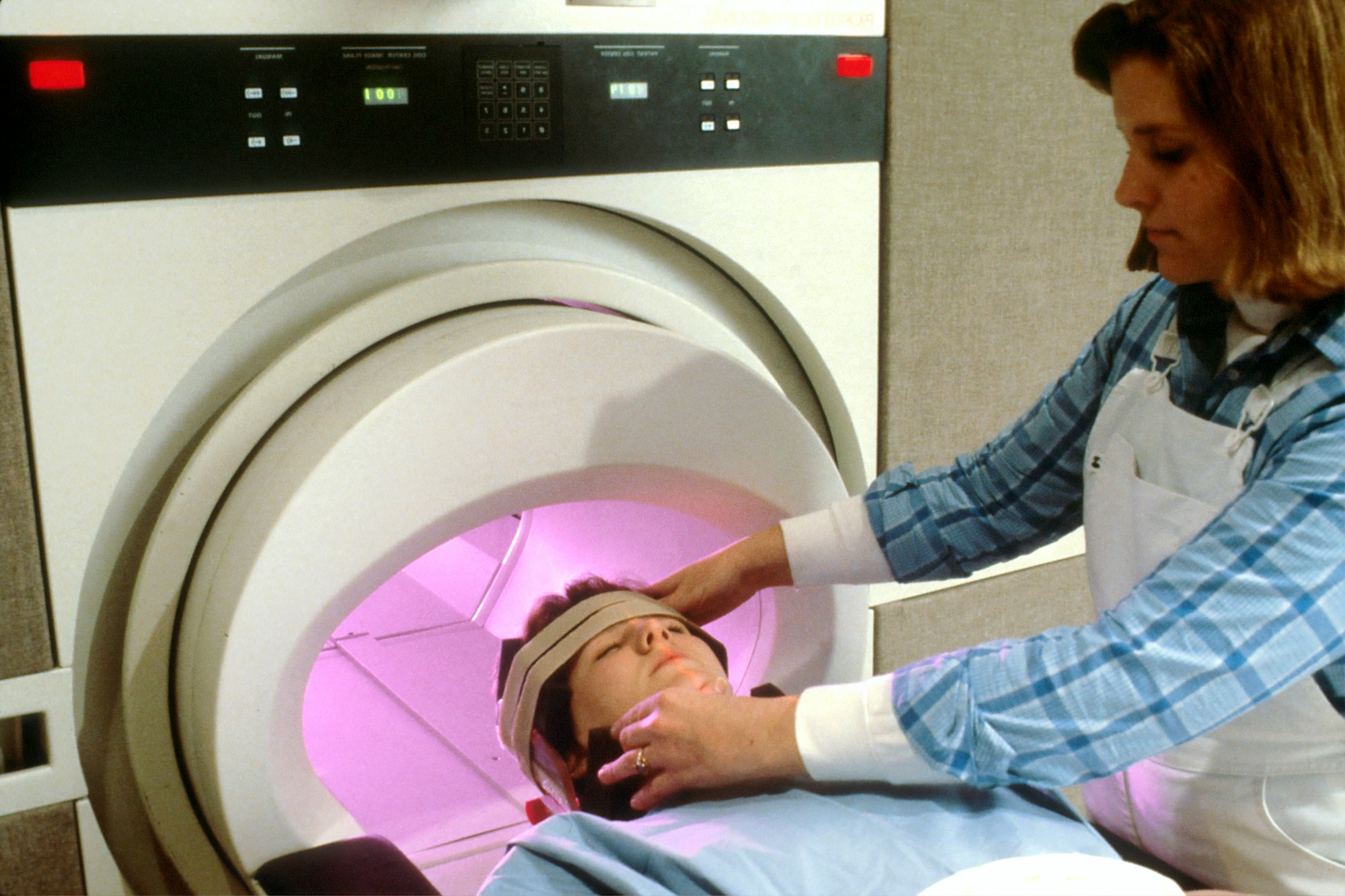

Diagnosing CBD
Diagnosing CBD requires a comprehensive approach, including a thorough clinical evaluation to assess movement symptoms, cognitive function, and speech difficulties. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays a pivotal role in this process, helping to detect changes in brain tissue such as cortical atrophy, a common feature in CBD. The MRI images can reveal shrinkage in specific brain regions, particularly the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia, which are critical in controlling movement and cognitive functions.
In some cases, a definitive diagnosis of CBD can only be confirmed through post-mortem analysis, where brain banks play a crucial role. The examination of brain tissue after death can provide invaluable information, revealing the presence of tau proteins and specific patterns of brain cell loss that are distinctive of CBD.
Clinical research continues to explore the tau protein and its gene, seeking to understand its role in CBD's pathology. Tau proteins, which are involved in maintaining the structure of nerve cells, accumulate abnormally in CBD, leading to cell death and the symptoms observed in the disorder.
Corticobasal degeneration clinical trial
While there is currently no cure for CBD, clinical trials are ongoing to explore potential treatments. Management of CBD symptoms often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including physical therapy to address movement disorders, occupational therapy to help with daily activities, and speech therapy for communication challenges. Medications like muscle relaxants and botulinum toxin can be prescribed to alleviate muscle rigidity and spasms, and in some cases, cholinesterase inhibitors may be used, although their effectiveness varies.
As CBD progresses, patients and their families face increasing challenges. From dealing with complex motor symptoms to navigating cognitive and speech difficulties, the journey with CBD is marked by a need for comprehensive care and support. Early detection and a detailed understanding of its symptoms are crucial for providing the best possible management for those living with this rare and challenging disease.
The Role of Tau Proteins in CBD
CBD is closely associated with abnormal accumulations of tau protein in the brain. These tau proteins, which form neurofibrillary tangles, are believed to play a crucial role in the degeneration of brain cells in CBD. Research into the tau gene and its mutations is vital for understanding the disease's pathogenesis and developing targeted treatments.
Managing CBD: Therapies and Support
Currently, there is no cure for CBD, but various therapies can help manage its symptoms. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy are crucial in helping patients maintain function and independence for as long as possible. In some cases, medications like muscle relaxants and botulinum toxin can alleviate muscle rigidity and spasms.
Living with CBD: Personal Experiences and Caregiving
The impact of CBD extends beyond the patients to their families and caregivers. Personal accounts, like those of Gary Radin and his mother, Lisa, who lost Neil Radin to CBD, highlight the diverse challenges faced by families. Caregivers often experience high stress levels, especially in managing complex symptoms like behavioral changes and movement problems. Support groups and resources like "What If It's Not Alzheimer's?: A Caregiver's Guide To Dementia" play a crucial role in providing information and support.

Advancements in Clinical Research and Trials
Ongoing clinical research and trials are crucial in the fight against CBD. These studies aim to understand the disease better, explore new treatments, and improve diagnostic criteria. For instance, the National Institutes for Health's grant to study frontotemporal degeneration represents a significant step in understanding related disorders.
Navigating the Complexities of CBD
CBD is a multifaceted disease, presenting a range of symptoms from motor dysfunctions to cognitive decline. It's essential for healthcare providers to recognize the specific symptoms of CBD to provide accurate diagnoses and appropriate care. Moreover, raising awareness about this rare disease is vital for early detection and better management.
Corticobasal Degeneration is a rare but life-altering disease that demands more attention and research. Through continued clinical trials, support for families, and a deeper understanding of its pathophysiology, there is hope for better management and eventual treatment breakthroughs. As we learn more about diseases like CBD, we inch closer to a world where dementia's impact is significantly reduced, offering a better quality of life for those affected.
Our Resources section can help you find the information and tools that you need. We have courses, videos, checklists, guidebooks, cheat sheets, how-to guides and more.
You can get started by clicking on the link below. We know that taking care of a loved one is hard work, but with our help you can get the support that you need.
Click here to go to Resources Section now!



