Can Sleep Apnea Cause High Blood Pressure?
Sleep apnea, a common sleep disorder, may significantly raise the risk of hypertension. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) causes blocked airways, leading to increased blood pressure and heightened risks of heart disease. Learn the link, effects, and treatments today.

High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition affecting millions of people across the world. It is caused by the narrowing of the arteries, resulting in an increase in blood pressure against the artery walls.
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder affecting millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep and can have a serious impact on overall health. Recent research has shown that there is a possible link between sleep apnea and high blood pressure.
People with sleep apnea, particularly those with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), are four times more likely to suffer from hypertension than those without this condition. This is because when the airways become blocked during sleep, the body must work harder to take in oxygen, resulting in an increase in blood pressure. Long-term elevations in blood pressure can lead to an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
It is important to understand the connection between sleep apnea and high blood pressure in order to ensure early diagnosis and treatment. This guide will provide an overview of the link between sleep apnea and hypertension, as well as the effects, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of both conditions.
This video explains sleep apnea in simple terms
Definition of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a disorder that results in pauses in breathing during sleep. These pauses can last anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes and can occur dozens of times an hour. This interruption of normal breathing can lead to decreased oxygen levels in the blood, which can have serious health consequences.
Sleep apnea has several causes, including being overweight or obese, a larger than normal neck circumference, nasal congestion that blocks the airways, sleeping on your back, and certain physical characteristics like a curved soft palate or enlarged tonsils. Sleep apnea can also be caused by medical conditions such as heart failure, stroke, and diabetes.
Central sleep apnea (CSA) differs from obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in that it involves lapses in breathing due to communication issues between the brain and breathing muscles. Unlike OSA, which is caused by physical blockages in the airway, CSA is related to the brain's failure to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. This can have significant cardiovascular implications, including effects on blood pressure and an increased risk of heart complications.
The Relationship Between Sleep Apnea and Blood Pressure
Sleep apnea and blood pressure are closely linked, with studies showing that people with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are more likely to develop high blood pressure. The relationship between sleep apnea and blood pressure is complex, but research suggests that the severity of OSA is a significant predictor of high blood pressure. In fact, studies have shown that up to 50% of people with OSA also have high blood pressure. This connection is due to the repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, which cause the body to experience stress and increase blood pressure levels. Understanding this relationship is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management of both conditions.
Effects of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that can have a significant effect on your health. It is characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, resulting in fragmented and poor quality sleep. Not only can it make you feel tired during the day, but it can also have physical health effects, including an increased risk of high blood pressure. Blood pressure dipping, the natural decrease in blood pressure during sleep, is generally between 10 and 20%. Individuals with severe obstructive sleep apnea may exhibit a nondipping pattern, leading to higher cardiovascular risks.
Common symptoms of sleep apnea include snoring, gasping for air during sleep, interrupted breathing for at least 10 seconds, and waking up with headaches and a dry mouth. If left untreated, sleep apnea can increase your risk of developing high blood pressure, heart attack, stroke, diabetes, depression, anxiety, and other long-term health problems.
If you are concerned that you may be suffering from sleep apnea, it is important to seek medical advice and get tested. A diagnosis as early as possible can help to reduce the risk of long-term health risks.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a medical condition where the force of your blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. There are several lifestyle and environmental factors that can cause or contribute to the development of high blood pressure. Some of the more common causes include:
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking can raise your blood pressure by narrowing your arteries, reducing the amount of blood flow in your body.
- Unhealthy Diet: Eating a diet that is high in salt, fats, and cholesterol can increase your blood pressure levels.
- Lack of Exercise: A sedentary lifestyle leads to an increased risk of developing high blood pressure.
- Alcohol Consumption: Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can lead to elevated blood pressure.
- Stress: Chronic stress can cause an increase in both your heart rate and blood pressure.
- Age: As you age, your blood vessels become less flexible and are unable to relax, which increases your blood pressure.
- Family History: If you have family members who have had high blood pressure, it could potentially increase your risk of having it as well.
It’s important to understand the causes of high blood pressure, as this can be the first step in preventing and managing this condition. If any of these lifestyle and environmental factors are causing your high blood pressure, making changes to reduce these risks may help to lower your blood pressure and reduce the need for medication.
How Sleep Apnea Affects the Body
Sleep apnea can have a significant impact on the body, particularly on the cardiovascular system. When a person with sleep apnea stops breathing during sleep, their body experiences a range of physiological changes, including increased heart rate, blood pressure, and stress hormones. These changes can lead to inflammation, oxidative stress, and damage to the blood vessels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Over time, these repeated episodes can strain the heart and blood vessels, leading to long-term health issues such as hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. Recognizing these effects underscores the importance of treating sleep apnea to protect overall health.
Medical Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a serious and potentially life-threatening sleep disorder that affects the normal breathing pattern during sleep. To properly diagnose sleep apnea and determine its effect on blood pressure, your doctor may use several tests.
The first step in diagnosing sleep apnea is a physical exam that involves taking your medical history, conducting a physical examination, and completing other assessments. Your doctor may also order an overnight sleep study, also known as a polysomnogram, to observe how your body is functioning during sleep.
A polysomnogram measures oxygen levels in your blood, heart rate, body movements, and other indicators of your health during sleep. Depending on the results, your doctor may prescribe a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine to provide air flow while you sleep.
Other tests your doctor may order to diagnose sleep apnea and determine its effect on blood pressure include an electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests, and imaging scans of the head and neck. Your doctor may also ask you to fill out a questionnaire to help identify any potential risk factors for the condition.
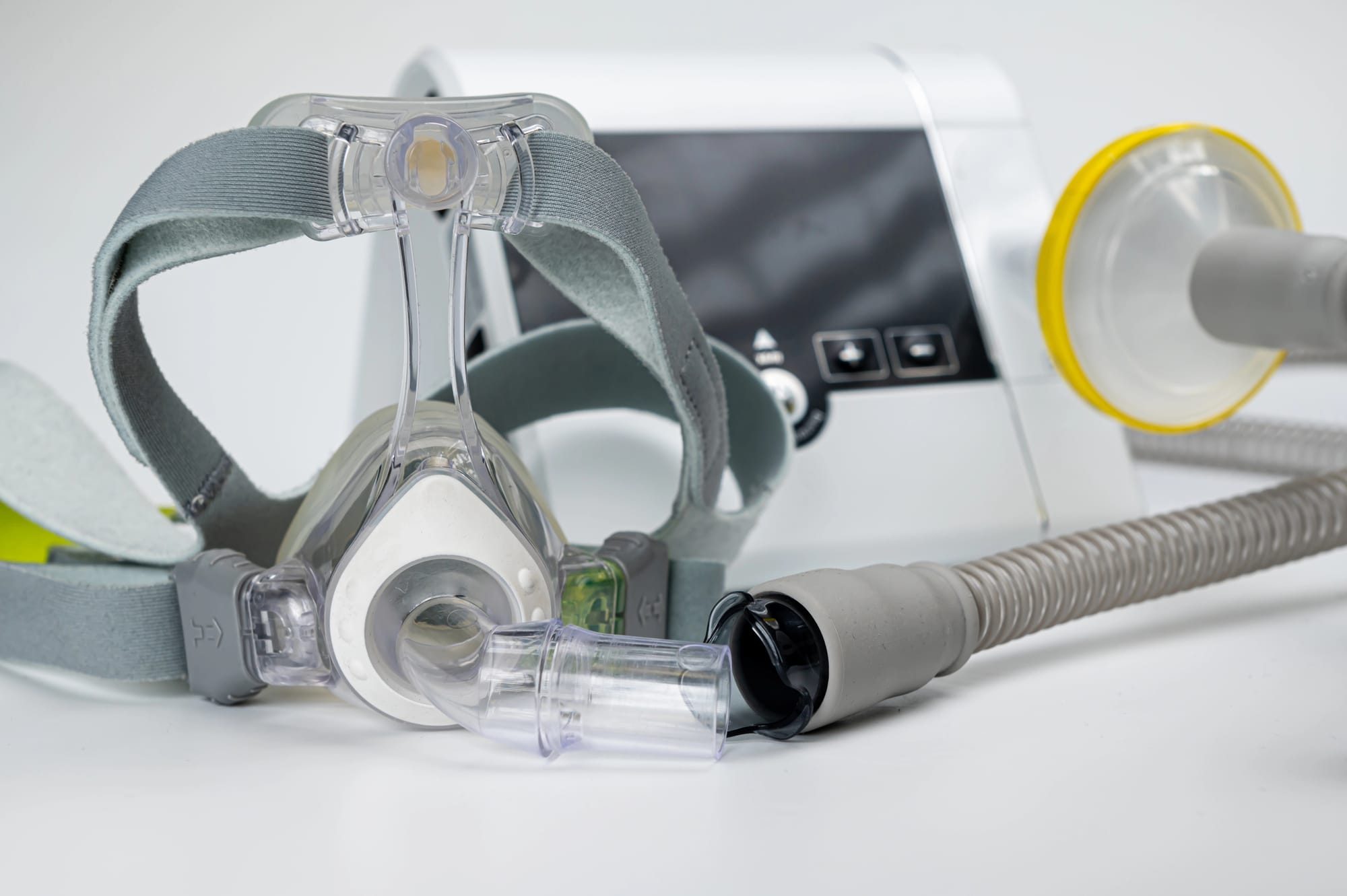
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment for Sleep Apnea
There are a number of treatments available to manage and reduce the symptoms of sleep apnea, which can also reduce high blood pressure. These treatments can include:
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) – this is a device worn at night which provides a continuous stream of air into the airway to keep it open. It can help to reduce the number of apneic episodes experienced throughout the night.
- Oral appliances – similar to a mouth guard, these are customised for the individual to ensure a correct fit. They work by supporting the jaw in a position that helps to keep the airway open during sleep.
- Surgery – certain conditions may require more invasive treatments such as removal of the tonsils or adenoids, or even a tracheostomy.
- Weight loss and lifestyle changes – making changes to your diet, exercising regularly, and reducing alcohol and caffeine intake can help to reduce the risk of sleep apnea, as can losing excess weight.
Treating sleep apnea can be an effective way to reduce the likelihood of developing high blood pressure or other health problems associated with sleep apnea. Contact your doctor to learn more about how to best treat your sleep apnea.
Effect of Sleep Apnea Treatment on Blood Pressure
Treating sleep apnea can have a significant impact on blood pressure levels. Studies have shown that continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, a common treatment for OSA, can lower daytime blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. In fact, a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that CPAP therapy reduced systolic blood pressure by an average of 10 mmHg in people with OSA. By maintaining an open airway during sleep, CPAP therapy helps to prevent the physiological changes that lead to elevated blood pressure, thereby improving overall cardiovascular health.
Managing Sleep Apnea-Associated Hypertension
Managing sleep apnea-associated hypertension requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, medical treatment, and sleep apnea therapy. Lifestyle changes such as weight loss, exercise, and stress reduction can help lower blood pressure levels, while medical treatment may include medications to control blood pressure. Sleep apnea therapy, such as CPAP or oral appliance therapy, can also help reduce blood pressure levels and improve overall health. By addressing both the sleep disorder and the hypertension, individuals can achieve better health outcomes and reduce the risk of serious complications.
High Blood Pressure Medication
High blood pressure caused by sleep apnea is typically treated with medication. There are a number of different types of medication prescribed, depending on the severity of the condition and other factors impacting blood pressure.
The most commonly prescribed medications for high blood pressure include diuretics, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and ACE inhibitors. Diuretics help reduce fluid retention, helping to decrease blood pressure. Beta-blockers work by blocking the effect of adrenaline, which helps reduce blood pressure. Calcium channel blockers impede the flow of calcium into the blood vessels, which in turn relaxes the walls of the arteries and helps to reduce blood pressure. Finally, ACE inhibitors reduce the production of angiotensin, which helps to lower blood pressure.
In some cases, combination therapy may be recommended; using two or more medications in order to achieve optimal results. A combination of lifestyle changes and medication may also be advised in order to reduce the risk of further complications of high blood pressure.
Behavioral Changes
Sleep apnea is a common condition and the high blood pressure it can cause can be managed with lifestyle changes. Making small changes to your daily activities can go a long way towards reducing its effects.
These lifestyle changes may include:
- Losing weight - If you are overweight, losing as little as 5% of your body weight can make a big difference.
- Quitting smoking - This can improve your overall health, as well as reduce the severity of sleep apnea.
- Avoiding alcohol and heavy meals before bedtime - Alcohol and heavy meals can worsen sleep apnea symptoms.
- Sleeping on your side - Sleeping on your back can exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms. Try sleeping on your side instead.
- Getting enough sleep - Aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep every night. Getting adequate rest helps to reduce daytime fatigue and improve concentration.
Making these lifestyle changes can help to reduce the effects of sleep apnea related high blood pressure. However, it is important to note that it is also important to seek medical advice to ensure that your condition is properly managed.
There are many different home remedies and therapies that can be used to reduce the severity of sleep apnea related high blood pressure. Some of these include:
- Regular exercise: Exercise helps to reduce stress levels, improve circulation, and reduce the risk of high blood pressure.
- Healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats can help to reduce the risk of high blood pressure.
- Relaxation techniques: Meditation, yoga, and other relaxation techniques can help to lower stress levels and improve sleep.
- Weight loss: Maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the severity of sleep apnea and associated high blood pressure.
- CPAP machine: Using a CPAP machine can help to reduce the severity of sleep apnea and associated high blood pressure.
These home remedies and therapies can help to alleviate the symptoms of sleep apnea related high blood pressure. It is important to discuss these treatments with your doctor before attempting to try them.
Health Complications of Untreated Sleep Apnea
Untreated sleep apnea can lead to a range of serious health complications, including cardiovascular disease, stroke, and atrial fibrillation. Sleep apnea can also increase the risk of acute sleep deprivation, which can impair cognitive function, mood, and overall quality of life. Furthermore, untreated sleep apnea can lead to increased blood pressure levels, which can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. The long-term effects of untreated sleep apnea highlight the importance of early diagnosis and effective treatment to prevent these potentially life-threatening complications.
Complications of High Blood Pressure
Having high blood pressure for a long period of time can put additional strain on your body and can lead to serious health problems. Some potential complications associated with long-term elevated blood pressure include:
- Stroke – High blood pressure can increase the risk of a stroke due to blood clots. A stroke may result in physical disabilities, memory loss or even death.
- Heart Disease – Long-term high blood pressure can cause the heart to become enlarged (hypertrophy) or even weaken. This increases the risk of heart attack, heart failure or other heart conditions.
- Kidney Damage – The arteries that supply the kidneys with oxygen can be damaged by high blood pressure, resulting in reduced kidney function.
- Vision Loss – High blood pressure can damage the optic nerve, leading to blurred or decreased vision.
If high blood pressure is left untreated, it can lead to serious and life-threatening complications. It is important to monitor your blood pressure regularly and seek medical attention if you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above.
Prevention of High Blood Pressure due to Sleep Apnea
There are a number of steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of high blood pressure due to sleep apnea. These include:
- Quitting smoking.
- Losing weight if you are overweight or obese.
- Reducing alcohol intake.
- Making sure to take regular breaks from work/study.
- Limiting caffeine and other stimulants.
- Monitoring your blood pressure and keeping track of any changes.
- Getting a minimum of 7-8 hours of quality sleep every night.
- Avoiding sleeping on your back.
- Using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine or other treatment device prescribed by a doctor.
- Seeking medical advice if you are having breathing difficulties at night.
By following these recommendations, you can help to reduce your risk of developing high blood pressure due to sleep apnea.
High blood pressure caused by sleep apnea is a serious condition that should not be underestimated. It can have far-reaching health consequences if left untreated for a long period of time. That is why it is so important to take the necessary steps to diagnose and treat sleep apnea related high blood pressure.
It is essential to understand the connection between sleep apnea and high blood pressure, to be aware of the risk factors and possible treatments, and to make necessary lifestyle changes to minimise the symptoms. If you believe you may be at risk of having or developing this condition, it is important to seek professional advice from a healthcare provider. With the right diagnosis and treatment plan, you can manage your blood pressure and greatly reduce the associated risks.
You might also like this article: