The 10 Most Common Types of Dementia and Their Causes
Learn about the most common types of dementia, including Alzheimer's, vascular dementia, and mixed dementia, as well as their causes and symptoms. We also discuss less common forms of dementia, such as Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease and Huntington's disease.
The 10 Most Common Types of Dementia and Their Causes
Dementia, a complex neurological condition, manifests in various forms, each with distinct causes and symptoms. Below, we delve into the ten most prevalent types of dementia, shedding light on their underlying causes:
1.Alzheimer’s Disease: Leading the list, Alzheimer's is a progressive disorder severely affecting cognitive functions. While the exact cause remains elusive, researchers attribute it to the accumulation of plaques and tangles, which inflict damage on brain cells, hampering their communication. This degradation leads to the erosion of social skills and intellectual capabilities.
2. Vascular Dementia: Emerging as the second most prevalent form, vascular dementia results from reduced blood flow to the brain. The deprivation of nutrients and oxygen to brain cells triggers their demise, thereby inducing dementia symptoms. Contributing medical conditions include diabetes, high blood pressure, and the narrowing of brain blood vessels.
3. Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB): Often mistaken for other forms, DLB is the second most common progressive dementia type. Linked to Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, DLB is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein deposits, Lewy bodies, within brain cells. These deposits hinder nerve cell communication, leading to impaired physical functioning, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes.
4. Mixed Dementia: A condition caused by multiple medical factors, mixed dementia, is typically a combination of Alzheimer's and vascular dementia. This occurrence is expected to rise with an aging population.
5. Parkinson’s Disease Dementia (PDD): Stemming from the progressive neurological disorder Parkinson's disease, PDD primarily affects cognitive functions in later stages. Lewy Body type dementia often develops in Parkinson's patients, alongside physical symptoms like tremors and muscle stiffness.
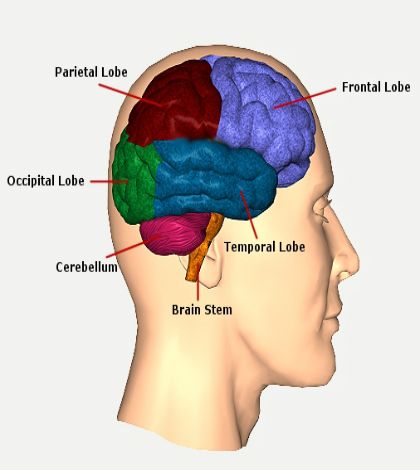
6. Frontotemporal Dementia (Pick’s Disease): A rare form, frontotemporal dementia leads to brain cell demise in the frontal and temporal lobes. It profoundly alters personality, social skills, and behaviors, with memory and speech issues emerging later.
7. Creutzfeldt-Jakob Dementia (CJD): An exceedingly rare form resembling mad cow disease, CJD is caused by a virus that disrupts normal brain function. Its swift progression is characterized by muscle stiffness, speech impairment, and coordination problems.
8. Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH): This dementia results from excess brain fluid buildup, applying pressure and affecting brain function. Symptoms include balance problems, speech difficulties, and memory impairments.
"Those with dementia are still people, and they still have stories, and they still have character, and they’re all individuals, and they’re all unique. And they just need to be interacted with on a human level". -Carey Mulligan
9. Huntington’s Disease: An inherited neurological dementia, Huntington’s disease gradually impacts movement, cognition, and behavior. Symptoms encompass impaired judgment, involuntary jerking, and memory deficits.
10. Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome: Often afflicting alcoholics due to thiamine (Vitamin B1) deficiency, this dementia results from malnutrition and certain medical conditions. It leads to confusion and impaired memory.
Diagnosing Dementia:
Identifying the specific type of dementia requires an exhaustive evaluation, including family history, medical background, and medication history. Comprehensive tests encompass physical assessments, urinalysis, blood tests, and potentially MRI scans. Family history and cognitive evaluations are also crucial elements in the diagnostic process.
Dementia stands as a complex realm that warrants meticulous understanding and compassionate engagement, respecting the uniqueness and stories of those it touches.
Our Resource section can help you find the information and tools that you need. We have courses, videos, checklists, guidebooks, cheat sheets, how-to guides and more.
You can get started by clicking on the link below. We know that taking care of a loved one is hard work, but with our help you can get the support that you need.
Click here to go to Resource Section now!
You might also like this article:






